The role of the msaABCR operon in implant-associated chronic osteomyelitis in Staphylococcus aureus USA300 LAC
- PMID: 33109085
- PMCID: PMC7590495
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-020-01964-8
The role of the msaABCR operon in implant-associated chronic osteomyelitis in Staphylococcus aureus USA300 LAC
Abstract
Background: The msaABCR operon regulates several staphylococcal phenotypes such as biofilm formation, capsule production, protease production, pigmentation, antibiotic resistance, and persister cells formation. The msaABCR operon is required for maintaining the cell wall integrity via affecting peptidoglycan cross-linking. The msaABCR operon also plays a role in oxidative stress defense mechanism, which is required to facilitate persistent and recurrent staphylococcal infections. Staphylococcus aureus is the most frequent cause of chronic implant-associated osteomyelitis (OM). The CA-MRSA USA300 strains are predominant in the United States and cause severe infections, including bone and joint infections.
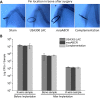
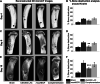
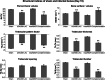
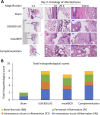
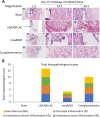
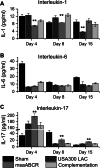
Results: The USA300 LAC strain caused significant bone damage, as evidenced by the presence of severe bone necrosis with multiple foci of sequestra and large numbers of multinucleated osteoclasts. Intraosseous survival and biofilm formation on the K-wires by USA300 LAC strains was pronounced. However, the msaABCR deletion mutant was attenuated. We observed minimal bone necrosis, with no evidence of intramedullary abscess and/or fibrosis, along reduced intraosseous bacterial population and significantly less biofilm formation on the K-wires by the msaABCR mutant. microCT analysis of infected bone showed significant bone loss and damage in the USA300 LAC and complemented strain, whereas the msaABCR mutant's effect was reduced. In addition, we observed increased osteoblasts response and new bone formation around the K-wires in the bone infected by the msaABCR mutant. Whole-cell proteomics analysis of msaABCR mutant cells showed significant downregulation of proteins, cell adhesion factors, and virulence factors that interact with osteoblasts and are associated with chronic OM caused by S. aureus.
Conclusion: This study showed that deletion of msaABCR operon in USA300 LAC strain lead to defective biofilm in K-wire implants, decreased intraosseous survival, and reduced cortical bone destruction. Thus, msaABCR plays a role in implant-associated chronic osteomyelitis by regulating extracellular proteases, cell adhesions factors and virulence factors. However additional studies are required to further define the contribution of msaABCR-regulated molecules in osteomyelitis pathogenesis.
Keywords: K-wire implants; Osteomyelitis; Staphylococcus aureus; Virulence factors; msaABCR operon.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



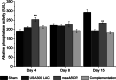
References
-
- Arnold SR, Elias D, Buckingham SC, Thomas ED, Novais E, Arkader A, Howard C. Changing patterns of acute hematogenous osteomyelitis and septic arthritis: emergence of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Pediatr Orthop. 2006;26(6):703–708. doi: 10.1097/01.bpo.0000242431.91489.b4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gwynne-Jones DP, Stott NS. Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a cause of musculoskeletal sepsis in children. J Pediatr Orthop. 1999;19(3):413–416. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

