Health literacy in the general population in the context of epidemic or pandemic coronavirus outbreak situations: Rapid scoping review
- PMID: 33109429
- PMCID: PMC7547635
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pec.2020.10.012
Health literacy in the general population in the context of epidemic or pandemic coronavirus outbreak situations: Rapid scoping review
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this rapid scoping review, for which only studies from the general population were considered, was to describe the extent of existing research on HL in the context of previous coronavirus outbreaks (SARS-CoV-1, MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2).
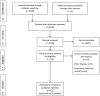
Methods: We searched major databases and included publications of quantitative and qualitative studies in English and German on any type of research on the functional, critical and communicative domains of HL conducted in the context of the three outbreaks in the general population. We extracted and tabulated relevant data and narratively reported where and when the study was conducted, the design and method used, and how HL was measured.
Results: 72 studies were included. Three investigated HL or explicitly referred to the concept of HL, 14 were guided by health behaviour theory. We did not find any study designed to develop or psychometrically evaluate pandemic/epidemic HL instruments, or relate pandemic/epidemic or general HL to a pandemic/epidemic outcome, or any controlled intervention study. Type of assessment of the domains of HL varied widely.
Conclusion: Theory-driven observational studies and interventions, examining whether pandemic-related HL can be improved are needed.
Practice implications: The development and validation of instruments that measure pandemic-related HL is desirable.
Keywords: Coronavirus; Epidemic; Health literacy; Pandemic; Scoping review.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors report no declarations of interest.
Comment in
-
Challenges for healthcare communication during the COVID-19 pandemic.Patient Educ Couns. 2021 Feb;104(2):215-216. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2021.01.006. Patient Educ Couns. 2021. PMID: 33518199 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organisation . 2020. Novel Coronavirus(2019-nCoV)SITUATION REPORT-121 JANUARY.https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2... (Accessed 20 May 2020)
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous