ZBP1 promotes fungi-induced inflammasome activation and pyroptosis, apoptosis, and necroptosis (PANoptosis)
- PMID: 33109609
- PMCID: PMC7939383
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015924
ZBP1 promotes fungi-induced inflammasome activation and pyroptosis, apoptosis, and necroptosis (PANoptosis)
Abstract
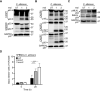
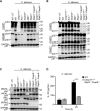
Candida albicans and Aspergillus fumigatus are dangerous fungal pathogens with high morbidity and mortality, particularly in immunocompromised patients. Innate immune-mediated programmed cell death (pyroptosis, apoptosis, necroptosis) is an integral part of host defense against pathogens. Inflammasomes, which are canonically formed upstream of pyroptosis, have been characterized as key mediators of fungal sensing and drivers of proinflammatory responses. However, the specific cell death pathways and key upstream sensors activated in the context of Candida and Aspergillus infections are unknown. Here, we report that C. albicans and A. fumigatus infection induced inflammatory programmed cell death in the form of pyroptosis, apoptosis, and necroptosis (PANoptosis). Further, we identified the innate immune sensor Z-DNA binding protein 1 (ZBP1) as the apical sensor of fungal infection responsible for activating the inflammasome/pyroptosis, apoptosis, and necroptosis. The Zα2 domain of ZBP1 was required to promote this inflammasome activation and PANoptosis. Overall, our results demonstrate that C. albicans and A. fumigatus induce PANoptosis and that ZBP1 plays a vital role in inflammasome activation and PANoptosis in response to fungal pathogens.
Keywords: Aspergillus fumigatus; Candida albicans; MLKL; PANoptosis; PANoptosome; RIPK3; ZBP1; apoptosis; caspase-1; caspase-3; caspase-7; caspase-8; cell death; fungi; gasdermin D; host defense; infection; infectious disease; inflammasome; necroptosis; pyroptosis.
© 2020 Banoth et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest—The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

