Cardiovascular disease risk assessment in patients with familial Mediterranean fever related renal amyloidosis
- PMID: 33110219
- PMCID: PMC7591897
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-75433-7
Cardiovascular disease risk assessment in patients with familial Mediterranean fever related renal amyloidosis
Abstract
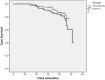
Chronic inflammation and proteinuria is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD) in patients with chronic kidney diseases and rheumatologic disorders. Our aim was to investigate the CVD events (CVDEs) and survival between the patients with FMF-related AA amyloidosis and glomerulonephropathies (GN) to define possible predictors for CVDEs. A prospective follow-up study with FMF-amyloidosis and glomerulonephropathy (GN) was performed and patients were followed for CVDEs. Flow-mediated dilatation (FMD), FGF-23, serum lipid, hsCRP levels, BMI and HOMA were assessed. A Cox regression analysis was performed to evaluate the risk factors for CVDEs. There were 107 patients in the FMF-amyloidosis group and 126 patients with GN group. Forty-seven CVDEs were observed during the 4.2-years follow up; all 28 patients in the FMF-amyloidosis group and 14/19 patients with GN developed CVDEs before the age of 40 (p = 0.002). CVD mortality was 2.8 times higher (95% CI 1.02-7.76) in patients with FMF-amyloidosis. Across both groups, FMD and FGF23 (p < 0.001) levels were independently associated with the risk of CVDEs. Patients with FMF-amyloidosis are at increased risk of early CVDEs with premature mortality age. FGF 23, FMD and hsCRP can stratify the risk of early CVD in patients with FMF-related AA amyloidosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endothelial function in patients with familial Mediterranean fever-related amyloidosis and association with cardiovascular events.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014 Nov;53(11):2002-8. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keu231. Epub 2014 Jun 6. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014. PMID: 24907154
-
The role of azurocidin in patients with familial Mediterranean fever and AA amyloidosis and its association with cardiovascular risk factors.Int Urol Nephrol. 2021 Mar;53(3):531-538. doi: 10.1007/s11255-020-02652-2. Epub 2020 Oct 15. Int Urol Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33058037
-
Association between basal proteinuria levels and pregnancy outcomes in familial Mediterranean fever.J Obstet Gynaecol. 2020 Nov;40(8):1102-1105. doi: 10.1080/01443615.2019.1700944. Epub 2020 Apr 9. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2020. PMID: 32270724
-
Tocilizumab in the treatment of twelve cases with aa amyloidosis secondary to familial mediterranean fever.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2017 May 30;12(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s13023-017-0642-0. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2017. PMID: 28558744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amyloid goiter in Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF): a clinicopathologic study of 10 cases.Ren Fail. 2001 Sep;23(5):659-67. doi: 10.1081/jdi-100107362. Ren Fail. 2001. PMID: 11725912 Review.
Cited by
-
Vascular function and arterial stiffness in multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children with Covid-19.ARYA Atheroscler. 2025;21(1):54-62. doi: 10.48305/arya.2025.43214.3008. ARYA Atheroscler. 2025. PMID: 40401207 Free PMC article.
-
Likelihood of amyloid formation in COVID-19-induced ARDS.Trends Microbiol. 2021 Nov;29(11):967-969. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2021.03.008. Epub 2021 Mar 29. Trends Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33795156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of Surrogate Markers for Cardiovascular Disease in Familial Mediterranean Fever-Related Amyloidosis Patients Homozygous for M694V Mutation in MEFV Gene.Life (Basel). 2022 Apr 25;12(5):631. doi: 10.3390/life12050631. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35629299 Free PMC article.
-
Intima media thickness of carotid arteries in familial Mediterranean fever: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Rheumatol. 2022 Dec;41(12):3769-3776. doi: 10.1007/s10067-022-06326-5. Epub 2022 Aug 6. Clin Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 35933450
-
Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidant, and Anti-Atherosclerotic Effects of Natural Supplements on Patients with FMF-Related AA Amyloidosis: A Non-Randomized 24-Week Open-Label Interventional Study.Life (Basel). 2022 Jun 15;12(6):896. doi: 10.3390/life12060896. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35743929 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical