Sox2 is necessary for androgen ablation-induced neuroendocrine differentiation from Pten null Sca-1+ prostate luminal cells
- PMID: 33110232
- PMCID: PMC7796948
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-020-01526-2
Sox2 is necessary for androgen ablation-induced neuroendocrine differentiation from Pten null Sca-1+ prostate luminal cells
Abstract
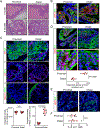
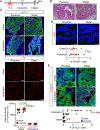
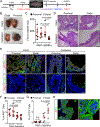
Prostate adenocarcinoma undergoes neuroendocrine differentiation to acquire resistance toward antihormonal therapies. The underlying mechanisms have been investigated extensively, among which Sox2 has been shown to play a critical role. However, genetic evidence in mouse models for prostate cancer to support the crucial role of Sox2 is missing. The adult mouse prostate luminal cells contain both castration-resistant Sox2-expressing Sca-1+ cells and castration-responsive Sca-1- cells. We show that both types of the luminal cell are susceptible to oncogenic transformation induced by loss of function of the tumor suppressor Pten. The tumors derived from the Sca-1+ cells are castration resistant and are more inclined to develop castration-induced neuroendocrine differentiation. Genetic ablation of Sox2 suppresses neuroendocrine differentiation but does not impact the castration-resistant property. This study provides direct genetic evidence that Sox2 is necessary for androgen ablation-induced neuroendocrine differentiation of Pten null prostate adenocarcinoma, corroborates that the lineage status of the prostate cancer cells is a determinant for its propensity to exhibit lineage plasticity, and supports that the intrinsic features of cell-of-origin for prostate cancers can dictate their clinical behaviors.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Davies AH, Beltran H, Zoubeidi A. Cellular plasticity and the neuroendocrine phenotype in prostate cancer. Nature reviews Urology. 2018;15(5):271–86. Epub 2018/02/21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

