Regulation of E2F1 activity via PKA-mediated phosphorylations
- PMID: 33110360
- PMCID: PMC7585165
- DOI: 10.3906/biy-2003-9
Regulation of E2F1 activity via PKA-mediated phosphorylations
Abstract
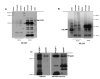
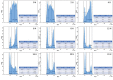
E2F1 becomes activated during the G1 phase of the cell cycle, and posttranslational modifications modulate its activity. Activation of G-protein coupled receptors (GPCR) by many ligands induces the activation of adenylate cyclases and the production of cAMP, which activates the PKA enzyme. Activated PKA elicits its biological effect by phosphorylating the target proteins containing serine or threonine amino acids in the RxxS/T motif. Since PKA activation negatively regulates cell proliferation, we thought that activated PKA would negatively affect the activity of E2F1. In line with this, when we analyzed the amino acid sequence of E2F1, we found 3 hypothetical consensus PKA phosphorylation sites located at 127-130, 232-235, and 361-364 positions and RYET, RLLS, and RMGS sequences. After showing the binding and phosphorylation of E2F1 by PKA, we converted the codons of Threonine-130, Serine-235, and Serine-364 to Alanine and Glutamic acid codons on the eukaryotic E2F1 expression vector we had previously created. We confirmed the phosphorylation of T130, S235, and S364 by developing monoclonal antibodies against phospho-specific forms of these sites and showed that their phosphorylation is cell cycle-dependent. According to our results, PKA-mediated phosphorylation of E2F1 by PKA inhibits proliferation and glucose uptake and induces caspase-3 activation and senescence.
Keywords: E2F1; PKA; cell cycle; forskolin; proliferation; senescence.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Anghileri P Branduardi P Sternieri F Monti P Visintin R Chromosome separation and exit from mitosis in budding yeast: dependence on growth revealed by cAMP-mediated inhibition. Experimental Cell Research . 1999;250:510–523. - PubMed
-
- Aoki I Higuchi M Gotoh Y NEDDylation controls the target specificity of E2F1 and apoptosis induction. Oncogene . 2013;32:3954–3964. - PubMed
-
- Bandara LR La Thangue NB Adenovirus E1a prevents the retinoblastoma gene product from complexing with a cellular transcription factor. Nature . 1991;351:494–497. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
