Association of HIVEP3 Gene and Lnc RNA with Femoral Neck Bone Mineral Content and Hip Geometry by Genome-Wide Association Analysis in Chinese People
- PMID: 33110425
- PMCID: PMC7579678
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/6929073
Association of HIVEP3 Gene and Lnc RNA with Femoral Neck Bone Mineral Content and Hip Geometry by Genome-Wide Association Analysis in Chinese People
Abstract
Purpose: GWAS has successfully located and analyzed the pathogenic genes of osteoporosis. Genetic studies have found that heritability of BMD is 50%-85% while the other half is caused by hip geometric parameters and tissue horizontal characteristics. This study was designed to study the GWAS of osteoporosis in Shanghai Han population.
Methods: We collected 1224 unrelated healthy young men (20-40 years old), young women (20-40 years old), and postmenopausal women (over 50 years old) who lived in Shanghai. BMD and hip geometric parameters were measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. The genomic DNA of peripheral blood was extracted and analyzed by using Illumina Human Asian Screening Array-24 + v1.0 (ASA) gene chip. Statistical analysis was carried out to evaluate the relationship between these SNPs and BMD and hip geometric parameters.
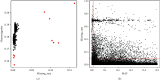
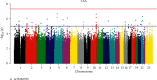
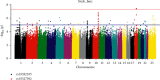
Results: A total of 1155 subjects were included. We found that one SNP rs35282355 located in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 enhancer-binding protein 3 gene (HIVEP3) and another 25 SNPs located in LINC RNA were significantly correlated with bone mineral content (BMC) in the femoral neck (P= 2.30 × 10-9, P < 5 × 10-8). We also found that the correlation between SNP rs35282355 and cross-sectional area (CSA) of hip geometry was a significant marginal statistical difference (P = 5.95 × 10-8).
Conclusions: Through this study, we found that HIVEP3 gene and LINC RNA are potentially correlated with femoral neck BMC. These results provide important information for us to further understand the etiology and genetic pathogenesis of osteoporosis. In the future, we will expand the sample size to verify these loci and carry out molecular research.
Copyright © 2020 Weiwei Hu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aged-Related Changes in Body Composition and Association between Body Composition with Bone Mass Density by Body Mass Index in Chinese Han Men over 50-year-old.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 19;10(6):e0130400. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130400. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26090818 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of bazedoxifene on bone structural strength evaluated by hip structure analysis.Bone. 2015 Aug;77:115-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2015.04.027. Epub 2015 Apr 23. Bone. 2015. PMID: 25917574 Clinical Trial.
-
Utilization of DXA Bone Mineral Densitometry in Ontario: An Evidence-Based Analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006;6(20):1-180. Epub 2006 Nov 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006. PMID: 23074491 Free PMC article.
-
Proximal Femoral Geometry as Fracture Risk Factor in Female Patients with Osteoporotic Hip Fracture.J Bone Metab. 2016 Aug;23(3):175-82. doi: 10.11005/jbm.2016.23.3.175. Epub 2016 Aug 31. J Bone Metab. 2016. PMID: 27622182 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of genetic variants of IL-6, IL6R, LRP5, ESR1 and SP7 genes on bone mineral density in postmenopausal Mexican-Mestizo women with obesity.Gene. 2013 Oct 10;528(2):216-20. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.07.008. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23891823
Cited by
-
Strong Genetic Effects on Bone Mineral Density in Multiple Locations with Two Different Techniques: Results from a Cross-Sectional Twin Study.Medicina (Kaunas). 2021 Mar 8;57(3):248. doi: 10.3390/medicina57030248. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021. PMID: 33800136 Free PMC article.
-
lincRNA00907 promotes NASH progression by targeting miRNA-942-5p/TAOK1.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Apr 10;16(8):6868-6882. doi: 10.18632/aging.205730. Epub 2024 Apr 10. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38613803 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the common loci for six body measurement traits in Chinese Wenshan cattle.Front Genet. 2023 Nov 24;14:1318679. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1318679. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 38075675 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

