A20-Binding Inhibitor of NF- κ B 1 Ameliorates Neuroinflammation and Mediates Antineuroinflammatory Effect of Electroacupuncture in Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Rats
- PMID: 33110436
- PMCID: PMC7582058
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/6980398
A20-Binding Inhibitor of NF- κ B 1 Ameliorates Neuroinflammation and Mediates Antineuroinflammatory Effect of Electroacupuncture in Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Rats
Abstract
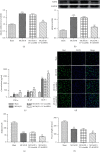
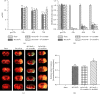
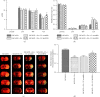
A20-binding inhibitor of NF-κB 1 (ABIN1) is an inhibitor of NF-κB and exerts anti-inflammatory effect. Electroacupuncture (EA) is considered as a neuroprotective strategy by inhibiting neuroinflammatory damage after cerebral ischemia. This study was performed to explore the role of ABIN1 and investigate whether the ABIN1 is involved in the mechanism of EA in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) rats. Male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were subjected to middle cerebral artery occlusion/reperfusion (MCAO/R) and received EA after reperfusion once a day. Lentivirus-mediated ABIN1 gene knockdown was used to detect the role of ABIN1 in neuroinflammation after I/R. ABIN1 expression, proinflammatory cytokine levels, microglial activation, neurological function, infarct volumes, and NF-κB activation were assessed. ABIN1 expression was elevated in the peri-infarct cortex and was further upregulated by EA. ABIN1 knockdown increased the levels of proinflammatory cytokines and activation of microglia, worsened neurological deficits, and enlarged the infarct volume. Moreover, ABIN1 was blocked to partially reverse the neuroprotective effect of EA, and this treatment weakened the ability of EA to suppress NF-κB activity. Based on these findings, ABIN1 is a potential suppressor of neuroinflammation and ABIN1 mediates the antineuroinflammatory effect of EA in cerebral I/R rats.
Copyright © 2020 Xueling Zhou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Upregulation of neuronal zinc finger protein A20 expression is required for electroacupuncture to attenuate the cerebral inflammatory injury mediated by the nuclear factor-kB signaling pathway in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion rats.J Neuroinflammation. 2016 Oct 3;13(1):258. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0731-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2016. PMID: 27716383 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture Suppresses the NF-κB Signaling Pathway by Upregulating Cylindromatosis to Alleviate Inflammatory Injury in Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Rats.Front Mol Neurosci. 2017 Nov 6;10:363. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00363. eCollection 2017. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29163038 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of Neuronal Cylindromatosis Expression is Essential for Electroacupuncture-Mediated Alleviation of Neuroinflammatory Injury by Regulating Microglial Polarization in Rats Subjected to Focal Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion.J Inflamm Res. 2021 May 20;14:2061-2078. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S307841. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 34045881 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupunctre improves motor impairment via inhibition of microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in the sensorimotor cortex after ischemic stroke.Life Sci. 2016 Apr 15;151:313-322. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2016.01.045. Epub 2016 Mar 14. Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 26979777
-
Lentivirus-mediated overexpression of OTULIN ameliorates microglia activation and neuroinflammation by depressing the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion rats.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Mar 15;15(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1117-5. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 29544517 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Electroacupuncture Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment Through the Inhibition of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation by Regulating Melatonin-Mediated Mitophagy in Stroke Rats.Neurochem Res. 2022 Jul;47(7):1917-1930. doi: 10.1007/s11064-022-03575-3. Epub 2022 Mar 18. Neurochem Res. 2022. PMID: 35301664
-
ATP2B1-AS1 Promotes Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Through Regulating the miR-330-5p/TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Oct 12;9:720468. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.720468. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34712659 Free PMC article.
-
The immunomodulatory mechanism of acupuncture treatment for ischemic stroke: research progress, prospects, and future direction.Front Immunol. 2024 May 2;15:1319863. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1319863. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38756772 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Relationship of Astrocytes and Microglia with Different Stages of Ischemic Stroke.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023;21(12):2465-2480. doi: 10.2174/1570159X21666230718104634. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37464832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Anti-Inflammatory Actions and Mechanisms of Acupuncture from Acupoint to Target Organs via Neuro-Immune Regulation.J Inflamm Res. 2021 Dec 21;14:7191-7224. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S341581. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 34992414 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

