Determinants and Prevention Strategies of Substance Abuse in Pacific Countries: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 33110632
- PMCID: PMC7577372
- DOI: 10.5001/omj.2020.128
Determinants and Prevention Strategies of Substance Abuse in Pacific Countries: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Objectives: People abuse substances like drugs, alcohol, and tobacco for different reasons, including pleasure, improved performance and vigilance, relief of depression, curbing hunger, and weight control. In this review, we sought to identify the determinants and prevention strategies that have been undertaken to minimize the issue of substance abuse.
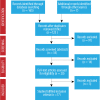
Methods: The systematic review was conducted following the Cochrane Library Guidelines and PRISMA checklist. We searched six online databases to identify studies from January 2000 to July 2017.
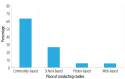
Results: Only peer-reviewed studies published in the English language that had full text accessible were included. We reviewed 19 studies; only one was quasi-experimental and the majority were descriptive studies. The determinants of substance abuse identified include personal, faciliatory/promotor, environmental, and social factors. The prevention strategies identified use culturally appropriate and gender-sensitive treatments, and identify sources of strength in families, community, individual, and even spiritual.
Conclusions: Substance abuse poses significant public health risks and therefore requires adequate interventions such as educating and informing individuals of the health risks associated with substance abuse and must be considered locally to promote the well-being of people.
Keywords: Prevention; Substance Abuse; Systematic Review.
The OMJ is Published Bimonthly and Copyrighted 2020 by the OMSB.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
The impact of knowledge on attitudes of emergency department staff towards patients with substance related presentations: a quantitative systematic review protocol.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Oct;13(10):133-45. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-2203. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26571289
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
Interventions for adults with a history of complex traumatic events: the INCiTE mixed-methods systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2020 Sep;24(43):1-312. doi: 10.3310/hta24430. Health Technol Assess. 2020. PMID: 32924926 Free PMC article.
-
Tobacco use: prevention, cessation, and control.Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2006 Jun;(140):1-120. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2006. PMID: 17764211 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of factors associated with adolescent substance use in Africa, 2000 to 2020.Addiction. 2025 Jun;120(6):1127-1142. doi: 10.1111/add.70023. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Addiction. 2025. PMID: 40016999 Free PMC article.
-
Proposing an integrative, dynamic and transdiagnostic model for addictions: dysregulation phenomena of the three main modes of the predostatic mind.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Jan 11;14:1298002. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1298002. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38274436 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gruber KJ, Taylor MF. A family perspective for substance abuse: Implications from the literature. J Soc Work Pract Addict 2006;6(1-2):1-29 .10.1300/J160v06n01_01 - DOI
-
- World Health Organisation [cited 2018 July] Available from: http://www.who.int/topics/substance_abuse/en/. 2017.
-
- Tabish S, Syed N, Syed N, Shah PS. Substance use disorder: a cultural catastrophe. Int J Sci Res (Ahmedabad) 2015;4(7):4.438.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources