Automated Segmentation of Retinal Fluid Volumes From Structural and Angiographic Optical Coherence Tomography Using Deep Learning
- PMID: 33110708
- PMCID: PMC7552937
- DOI: 10.1167/tvst.9.2.54
Automated Segmentation of Retinal Fluid Volumes From Structural and Angiographic Optical Coherence Tomography Using Deep Learning
Abstract
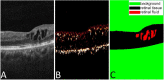
Purpose: We proposed a deep convolutional neural network (CNN), named Retinal Fluid Segmentation Network (ReF-Net), to segment retinal fluid in diabetic macular edema (DME) in optical coherence tomography (OCT) volumes.
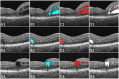
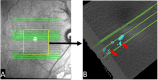
Methods: The 3- × 3-mm OCT scans were acquired on one eye by a 70-kHz OCT commercial AngioVue system (RTVue-XR; Optovue, Inc., Fremont, CA, USA) from 51 participants in a clinical diabetic retinopathy (DR) study (45 with retinal edema and six healthy controls, age 61.3 ± 10.1 (mean ± SD), 33% female, and all DR cases were diagnosed as severe NPDR or PDR). A CNN with U-Net-like architecture was constructed to detect and segment the retinal fluid. Cross-sectional OCT and angiography (OCTA) scans were used for training and testing ReF-Net. The effect of including OCTA data for retinal fluid segmentation was investigated in this study. Volumetric retinal fluid can be constructed using the output of ReF-Net. Area-under-receiver-operating-characteristic-curve, intersection-over-union (IoU), and F1-score were calculated to evaluate the performance of ReF-Net.
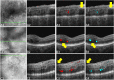
Results: ReF-Net shows high accuracy (F1 = 0.864 ± 0.084) in retinal fluid segmentation. The performance can be further improved (F1 = 0.892 ± 0.038) by including information from both OCTA and structural OCT. ReF-Net also shows strong robustness to shadow artifacts. Volumetric retinal fluid can provide more comprehensive information than the two-dimensional (2D) area, whether cross-sectional or en face projections.
Conclusions: A deep-learning-based method can accurately segment retinal fluid volumetrically on OCT/OCTA scans with strong robustness to shadow artifacts. OCTA data can improve retinal fluid segmentation. Volumetric representations of retinal fluid are superior to 2D projections.
Translational relevance: Using a deep learning method to segment retinal fluid volumetrically has the potential to improve the diagnostic accuracy of diabetic macular edema by OCT systems.
Keywords: OCT/OCTA; deep learning; retinal fluid volume; segmentation.
Copyright 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: Y. Guo, None; T.T. Hormel, None; H. Xiong, None; J. Wang, None; T.S. Hwang, None; Y. Jia, Optovue (F, P)
Figures





References
-
- Spaide RF. Retinal vascular cystoid macular edema: review and new theory. Retina. 2016; 36(10): 1823–1842. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez VH, Campbell J, Holekamp NM, et al. .. Early and long-term responses to anti–vascular endothelial growth factor therapy in diabetic macular edema: analysis of protocol I data. Am J Ophthalmol. 2016; 172: 72–79. - PubMed
-
- Nunes S, Pereira I, Santos A, Bernardes R, Cunha-Vaz J. Central retinal thickness measured with HD-OCT shows a weak correlation with visual acuity in eyes with CSME. Br J Ophthalmol. 2010; 94(9): 1201–1204. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

