Perception that Mothers and / or Guardians of Overweight or Obese Preschool Children Have of a Text Messaging Program to Support Behaviour Change in their Children
- PMID: 33110932
- PMCID: PMC7555567
- DOI: 10.1177/2333794X20961575
Perception that Mothers and / or Guardians of Overweight or Obese Preschool Children Have of a Text Messaging Program to Support Behaviour Change in their Children
Abstract
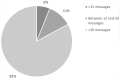
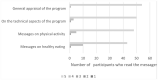
In most childhood obesity preventive programs, parents are targeted as they are key in achieving lifestyle behavior change in their children. Because their participation is generally low, new technologies, such as text messaging, are being tested to assess if their participation increases. The objective of this study was to determine the perception that mothers of overweight/ obese preschool children have of a textmessaging program developed to support their children's lifestyle behavior change. Text messages were sent to 60 mothers twice a week for 12 weeks; 58 of them said they received all of them. During the process mothers were contacted twice regarding their opinion on all aspects related to the messages. At follow-up, we determined perception by in depth interviews administered to participants. Results show that text messaging implemented in a personalized manner was considered successful in regards to providing useful information to support their children's behavior change.
Keywords: Obesity; change behaviour; text message; tools.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC) L, Abdeen ZA, Hamid Z, et al. Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: a pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128·9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet. 2017;390:627-642. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32129-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Savoye M, Shaw M, Dziura J, et al. Effects of a weight management program on body composition and metabolic parameters in overweight children: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2007;297:2697-2704. Accessed December 4, 2016 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17595270 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources