Serum Metabolomics for Biomarker Screening of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Esophageal Squamous Dysplasia Using Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
- PMID: 33110968
- PMCID: PMC7581083
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.0c02600
Serum Metabolomics for Biomarker Screening of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Esophageal Squamous Dysplasia Using Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
Background: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is one of the most common malignancies with poor diagnosis. Esophageal squamous dysplasia (ESD) is considered as an immediate precancerous lesion of ESCC. Lack of biomarkers for discriminating ESCC and ESD from healthy subjects limits the early diagnosis and treatment of ESCC. Therefore, a serum metabolomic strategy was conducted to identify and validate potential metabolic markers for the screening of ESCC and ESD subjects.
Methods: A total of 74 patients with ESCC, 72 patients with ESD, and 75 normal control (NC) subjects were enrolled in this study. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry was used to acquire serum metabolic profiles. Pathway analysis was conducted to uncover the fluctuated metabolic pathways during ESCC. Multivariate analyses were used to screen and validate the biomarkers.
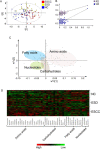
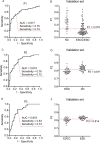
Results: ESCC, ESD, and NC subjects revealed progressively altered metabolic profiles, in which amino acids globally increased, while fatty acids decreased in ESCCs compared with the control groups. Pathway analysis demonstrated the activated biosynthesis of amino acids and inhibited desaturation of saturated fatty acids. The panel constructed with propanoic acid, linoleic acid, glycerol-3-phosphate, and l-glutamine showed the area under the curve (AUC), sensitivity, and specificity of 0.817, 0.75, and 0.74, respectively, in the discrimination of ESCC/ESD patients from NC subjects. The panel constructed by propanoic acid, l-leucine, and hydroxyproline revealed the AUC, sensitivity, and specificity of 0.819, 0.76, and 0.72, respectively, in the discrimination of ESD from NC subjects. The combination of hypoxanthine, 2-ketoisocaproic acid, l-glutamate, and l-aspartate showed the AUC, sensitivity, and specificity of 0.818, 0.83, and 0.74, respectively, in the discrimination of ESCC patients from ESD subjects.
Conclusions: Our study revealed the systematic landscape for metabolic alterations in sera of ESD and ESCC patients. The defined metabolite markers showed reasonable performance in the discrimination of ESCC and ESD patients, and may provide helpful reference for clinicians and biologists.
© 2020 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Plasma Metabolomics Reveals Diagnostic Biomarkers and Risk Factors for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Feb 7;12:829350. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.829350. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35198450 Free PMC article.
-
Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Discovers Dysregulated Metabolic Pathways and Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers.J Cancer. 2020 Apr 6;11(13):3944-3954. doi: 10.7150/jca.41733. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32328198 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Novel Circulating miRNA Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Squamous Dysplasia.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2019 Jul;28(7):1212-1220. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-18-1199. Epub 2019 Apr 15. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2019. PMID: 30988139
-
None-endoscopic Screening for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma- A Review.Middle East J Dig Dis. 2012 Apr;4(2):111-24. Middle East J Dig Dis. 2012. PMID: 24829644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic reprogramming in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jun 26;15:1423629. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1423629. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38989149 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolomic biomarkers in liquid biopsy: accurate cancer diagnosis and prognosis monitoring.Front Oncol. 2024 Feb 7;14:1331215. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1331215. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38384814 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of Fuhrman nuclear grade for clear cell renal carcinoma by a multi-information fusion model that incorporates CT-based features of tumor and serum tumor associated material.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Nov;149(17):15855-15865. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05353-2. Epub 2023 Sep 6. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37672076 Free PMC article.
-
Current status and perspectives of esophageal cancer: a comprehensive review.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2025 Mar;45(3):281-331. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12645. Epub 2024 Dec 26. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2025. PMID: 39723635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum metabolomics analysis for the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.J Cancer. 2021 Apr 2;12(11):3190-3197. doi: 10.7150/jca.54429. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33976728 Free PMC article.
-
A serum metabolomics analysis reveals a panel of screening metabolic biomarkers for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Clin Transl Med. 2021 May;11(5):e419. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.419. Clin Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34047482 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Wang G. Q.; Abnet C. C.; Shen Q.; Lewin K. J.; Sun X. D.; Roth M. J.; Qiao Y. L.; Mark S. D.; Dong Z. W.; Taylor P. R.; Dawsey S. M. Histological precursors of oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma: results from a 13 year prospective follow up study in a high risk population. Gut 2005, 54, 187–192. 10.1136/gut.2004.046631. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

