Human recombinant lysosomal β-Hexosaminidases produced in Pichia pastoris efficiently reduced lipid accumulation in Tay-Sachs fibroblasts
- PMID: 33111489
- PMCID: PMC8045741
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.c.31849
Human recombinant lysosomal β-Hexosaminidases produced in Pichia pastoris efficiently reduced lipid accumulation in Tay-Sachs fibroblasts
Abstract
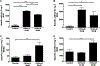
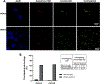
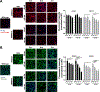
GM2 gangliosidosis, Tay-Sachs and Sandhoff diseases, are lysosomal storage disorders characterized by the lysosomal accumulation of GM2 gangliosides. This accumulation is due to deficiency in the activity of the β-hexosaminidases Hex-A or Hex-B, which are dimeric hydrolases formed by αβ or ββ subunits, respectively. These disorders show similar clinical manifestations that range from mild systemic symptoms to neurological damage and premature death. There is still no effective therapy for GM2 gangliosidoses, but some therapeutic alternatives, as enzyme replacement therapy, have being evaluated. Previously, we reported the production of active human recombinant β-hexosaminidases (rhHex-A and rhHex-B) in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. In this study, we evaluated in vitro the cellular uptake, intracellular delivery to lysosome, and reduction of stored substrates. Both enzymes were taken-up via endocytic pathway mediated by mannose and mannose-6-phosphate receptors and delivered to lysosomes. Noteworthy, rhHex-A diminished the levels of stored lipids and lysosome mass in fibroblasts from Tay-Sachs patients. Overall, these results confirm the potential of P. pastoris as host to produce recombinant β-hexosaminidases intended to be used in the treatment of GM2 gangliosidosis.
Keywords: GM2 gangliosidosis; Pichia pastoris; enzyme replacement therapy; recombinant hexosaminidases.
© 2020 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTERESTS
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

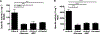
References
-
- Akeboshi H, Chiba Y, Kasahara Y, Takashiba M, Takaoka Y, Ohsawa M, … Jigami Y (2007). Production of recombinant beta-hexosaminidase A, a potential enzyme for replacement therapy for Tay-Sachs and Sandhoff diseases, in the methylotrophic yeast Ogataea minuta. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73(15), 4805–4812. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00463-07 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

