Targeting Crucial Host Factors of SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 33112126
- PMCID: PMC7605336
- DOI: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00456
Targeting Crucial Host Factors of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
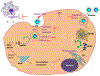
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has spread worldwide since its first incidence in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. Although the case fatality rate of COVID-19 appears to be lower than that of SARS and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS), the higher transmissibility of SARS-CoV-2 has caused the total fatality to surpass other viral diseases, reaching more than 1 million globally as of October 6, 2020. The rate at which the disease is spreading calls for a therapy that is useful for treating a large population. Multiple intersecting viral and host factor targets involved in the life cycle of the virus are being explored. Because of the frequent mutations, many coronaviruses gain zoonotic potential, which is dependent on the presence of cell receptors and proteases, and therefore the targeting of the viral proteins has some drawbacks, as strain-specific drug resistance can occur. Moreover, the limited number of proteins in a virus makes the number of available targets small. Although SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 share common mechanisms of entry and replication, there are substantial differences in viral proteins such as the spike (S) protein. In contrast, targeting cellular factors may result in a broader range of therapies, reducing the chances of developing drug resistance. In this Review, we discuss the role of primary host factors such as the cell receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), cellular proteases of S protein priming, post-translational modifiers, kinases, inflammatory cells, and their pharmacological intervention in the infection of SARS-CoV-2 and related viruses.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; coronavirus; drug targets; host factors; inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

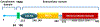
References
-
- Zhou P; Yang X-L; Wang X-G; Hu B; Zhang L; Zhang W; Si H-R; Zhu Y; Li B; Huang C-L; Chen H-D; Chen J; Luo Y; Guo H; Jiang R-D; Liu M-Q; Chen Y; Shen X-R; Wang X; Zheng X-S; Zhao K; Chen Q-J; Deng F; Liu L-L; Yan B; Zhan F-X; Wang Y-Y; Xiao G-F; Shi Z-L A Pneumonia Outbreak Associated with a New Coronavirus of Probable Bat Origin. Nature 2020, 579 (7798), 270–273. 10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen N; Zhou M; Dong X; Qu J; Gong F; Han Y; Qiu Y; Wang J; Liu Y; Wei Y; Xia J; Yu T; Zhang X; Zhang L Epidemiological and Clinical Characteristics of 99 Cases of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A Descriptive Study. The Lancet 2020, 395 (10223), 507–513. 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huang C; Wang Y; Li X; Ren L; Zhao J; Hu Y; Zhang L; Fan G; Xu J; Gu X; Cheng Z; Yu T; Xia J; Wei Y; Wu W; Xie X; Yin W; Li H; Liu M; Xiao Y; Gao H; Guo L; Xie J; Wang G; Jiang R; Gao Z; Jin Q; Wang J; Cao B Clinical Features of Patients Infected with 2019 Novel Coronavirus in Wuhan, China. The Lancet 2020, 395 (10223), 497–506. 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

