Refractory ulcerations associated with livedoid vasculopathy successfully treated with tofacitinib
- PMID: 33112475
- PMCID: PMC7816240
- DOI: 10.1111/dth.14470
Refractory ulcerations associated with livedoid vasculopathy successfully treated with tofacitinib
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
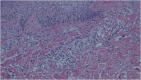
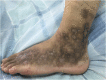
Figures

References
-
- Kumar A, Sharma A, Agarwal A. Livedoid vasculopathy presenting with leg ulcers. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019;58(11):2076. - PubMed
-
- Gardette E, Moguelet P, Bouaziz JD, et al. Livedoid vasculopathy: a French observational study including therapeutic options. Acta Derm Venereol. 2018;98(9):842‐847. - PubMed
-
- Kelly RI, Wee E, Tancharoen C, Tam MM, Balta S, Williams RA. Three cases of lymphocytic thrombophilic arteritis presenting with an annular eruption. Australas J Dermatol. 2018;59(2):e127‐e132. - PubMed
-
- Irani‐Hakime NA, Stephan F, Kreidy R, Jureidini I, Almawi WY. Livedoid vasculopathy associated with combined prothrombin G20210A and factor V (Leiden) heterozygosity and MTHFR C677T homozygosity. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2008;26(1):31‐34. - PubMed
-
- Gao Y, Jin H. Efficacy of an anti‐TNF‐alpha agent in refractory livedoid vasculopathy: a retrospective analysis. Dermatol Treat. 2020;1‐6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

