The role of the cytoskeletal proteins MreB and FtsZ in multicellular cyanobacteria
- PMID: 33112491
- PMCID: PMC7714070
- DOI: 10.1002/2211-5463.13016
The role of the cytoskeletal proteins MreB and FtsZ in multicellular cyanobacteria
Abstract
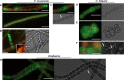
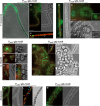
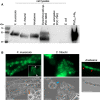
Multiseriate and true-branching cyanobacteria are at the peak of prokaryotic morphological complexity. However, little is known about the mechanisms governing multiplanar cell division and morphogenesis. Here, we study the function of the prokaryotic cytoskeletal proteins, MreB and FtsZ in Fischerella muscicola PCC 7414 and Chlorogloeopsis fritschii PCC 6912. Vancomycin and HADA labeling revealed a mixed apical, septal, and lateral trichome growth mode in F. muscicola, whereas C. fritschii exhibits septal growth. In all morphotypes from both species, MreB forms either linear filaments or filamentous strings and can interact with FtsZ. Furthermore, multiplanar cell division in F. muscicola likely depends on FtsZ dosage. Our results lay the groundwork for future studies on cytoskeletal proteins in morphologically complex cyanobacteria.
Keywords: Cyanobacteria; FtsZ; MreB; Stigonematales; cytoskeleton; morphogenesis.
© 2020 The Authors. Published by FEBS Press and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Kruse T, Bork‐Jensen J and Gerdes K (2005) The morphogenetic MreBCD proteins of Escherichia coli form an essential membrane‐bound complex. Mol Microbiol 55, 78–89. - PubMed
-
- Domínguez‐Escobar J, Chastanet A, Crevenna AH, Fromion V, Wedlich‐Söldner R and Carballido‐López R (2011) Processive movement of MreB‐associated cell wall biosynthetic complexes in bacteria. Science 333, 225–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

