Forecasting the type 2 diabetes mellitus epidemic and the role of key risk factors in Oman up to 2050: Mathematical modeling analyses
- PMID: 33112504
- PMCID: PMC8264408
- DOI: 10.1111/jdi.13452
Forecasting the type 2 diabetes mellitus epidemic and the role of key risk factors in Oman up to 2050: Mathematical modeling analyses
Abstract
Aims/introduction: To investigate and forecast type 2 diabetes mellitus epidemic, its related risk factors and cost in Oman by 2050.
Materials and methods: An age-structured mathematical model was used to characterize type 2 diabetes mellitus epidemiology and trends in Oman between 1990 and 2050. The model was parametrized using current and quality data, including six nationally representative population-based epidemiological surveys for type 2 diabetes mellitus and its key risk factors.
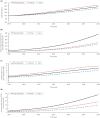
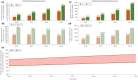
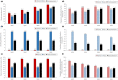
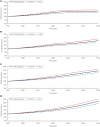
Results: The projected type 2 diabetes mellitus prevalence increased from 15.2% in 2020 to 23.8% in 2050. The prevalence increased from 16.8 and 13.8% in 2020 among women and men to 26.3 and 21.4% in 2050, respectively. In 2020, 190,489 Omanis were living with type 2 diabetes mellitus compared with 570,227 in 2050. The incidence rate per 1,000 person-years changed from 8.3 in 2020 to 12.1 in 2050. Type 2 diabetes mellitus' share of Oman's national health expenditure grew by 36% between 2020 and 2050 (from 21.2 to 28.8%). Obesity explained 56.7% of type 2 diabetes mellitus cases in 2020 and 71.4% in 2050, physical inactivity explained 4.3% in 2020 and 2.7% in 2050, whereas smoking accounted for <1% of type 2 diabetes mellitus cases throughout 2020-2050. Sensitivity and uncertainty analyses affirmed these predictions.
Conclusions: The type 2 diabetes mellitus epidemic in Oman is expected to increase significantly over the next three decades, consuming nearly one-third of the national health expenditure. The type 2 diabetes mellitus burden is heavily influenced by obesity. Interventions targeting this single risk factor should be a national priority to reduce and control the burden of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Oman.
Keywords: Forecasting model; Non-communicable disease; Risk factor.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Diabetes Investigation published by Asian Association for the Study of Diabetes (AASD) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- International Diabetes Federation . IDF Diabetes Atlas, 9th edn. International Diabetes Federation, 2019. Available from: https://www.diabetesatlas.org/upload/resources/2019/IDF_Atlas_9th_Editio.... Accessed November 24, 2019.
-
- World Health Organization . The Global Burden of Disease: 2004 Update. Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2008. Available from: http://www.who.int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/GBD_report_2004updat...).
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

