PARP1 Gene Polymorphisms and the Prognosis of Esophageal Cancer Patients from Cixian High-Incidence Region in Northern China
- PMID: 33112558
- PMCID: PMC7798169
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.10.2987
PARP1 Gene Polymorphisms and the Prognosis of Esophageal Cancer Patients from Cixian High-Incidence Region in Northern China
Abstract
Objective: Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1), as a key enzyme in the base excision repair pathway, plays a crucial role in tumorigenesis and progression. This study aimed to assess whether polymorphisms of PARP1 gene could be used as predictive biomarkers for the survival of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) patients from Cixian high-incidence region in northern China.
Methods: In 203 ESCC patients with survival information, PARP1 rs1136410 T/C and rs8679 T/C single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were genotyped by polymerase chain reaction ligase detection reaction (PCR-LDR) method. All statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS ver. 22.0 software package (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA).
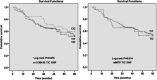
Results: The mean age ± standard deviation of the ESCC patients was 60.4 ± 7.9 years. There was no significant relation of sex, age, smoking status and upper gastrointestinal cancer family history with the survival time of the ESCC patients. The mean survival time of rs1136410 T/T, T/C and C/C genotype carriers were 43.3, 42.3 and 46.6 months, respectively. The rs1136410 was not associated with the survival time of the ESCC patients. For rs8679, the mean survival time of T/T genotype carriers was 43.7 months, which was not significantly different from that of the patients with T/C genotype (42.1 months).
Conclusion: In Cixian high-incidence region from northern China, rs1136410 and rs8679 SNPs might not be used to predict survival of ESCC patients. There is a need to explore whether other SNPs of PARP1 gene have an effect on prognosis of ESCC patients.
Keywords: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1; Polymorphism; Prognosis; survival.
Figures
References
-
- Cottet F, Blanché H, Verasdonck P, et al. New polymorphisms in the human poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 coding sequence: lack of association with longevity or with increased cellular poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation capacity. J Mol Med (Berl) 2000;78:431–40. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous