Highly Enantioselective Epoxidation of α,β-Unsaturated Ketones Using Amide-Based Cinchona Alkaloids as Hybrid Phase-Transfer Catalysts
- PMID: 33112627
- PMCID: PMC7660942
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c03272
Highly Enantioselective Epoxidation of α,β-Unsaturated Ketones Using Amide-Based Cinchona Alkaloids as Hybrid Phase-Transfer Catalysts
Abstract
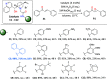
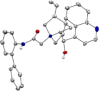
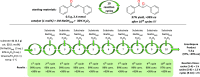
A series of 20 one chiral epoxides were obtained with excellent yields (up to 99%) and enantioselectivities (up to >99% ee) using hybrid amide-based Cinchona alkaloids. Our method is characterized by low catalyst loading (0.5 mol %) and short reaction times. Moreover, the epoxidation process can be carried out in 10 cycles, without further catalyst addition to the reaction mixture. This methodology significantly enhance the scale of the process using very low catalyst loading.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


References
-
- Katsuki T.; Sharpless K. B. The first practical method for asymmetric epoxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 5974–5976. 10.1021/ja00538a077. - DOI
- Gao Y.; Hanson R. M.; Klunder J. M.; Ko S. Y.; Masamune H.; Sharpless K. B. Catalytic asymmetric epoxidation and kinetic resolution: modified procedures including in situ derivatization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 109, 5765–5780. 10.1021/ja00253a032. - DOI
-
- Seayad J.; List B. Asymmetric organocatalysis. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2005, 3, 719–724. 10.1039/b415217b. - DOI - PubMed
- Hughes D. L. Asymmetric Organocatalysis in Drug Development—Highlights of Recent Patent Literature. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2018, 20, 574–584. 10.1021/acs.oprd.8b00096. - DOI
- Carlone A.; Bernardi L. Enantioselective organocatalytic approaches to active pharmaceutical ingredients – selected industrial examples. Phys. Sci. Rev. 2019, 4, 20180097. 10.1515/psr-2018-0097. - DOI
-
-
See
- Gorzynski Smith J. Synthetically Useful Reactions of Epoxides. Synthesis 1984, 629–656. 10.1055/s-1984-30921. - DOI
- Lauret C. Epoxy ketones as versatile building blocks in organic synthesis. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2001, 12, 2359–2383. 10.1016/S0957-4166(01)00412-8. - DOI
- Marco-Contelles J.; Molina M. T.; Anjum S. Naturally Occurring Cyclohexane Epoxides: Sources, Biological Activities, and Synthesis. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 2857. 10.1021/cr980013j. - DOI - PubMed
- Miyashita K.; Imanishi T. Syntheses of Natural Products Having an Epoxyquinone Structure. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 4515–4536. 10.1021/cr040613k. - DOI - PubMed
-
-
- Besse P.; Veschambre H. Chemical and biological synthesis of chiral epoxides. Tetrahedron 1994, 50, 8885–8927. 10.1016/S0040-4020(01)85362-X. - DOI
- Xia Q.-H.; Ge H. Q.; Ye C. P.; Liu Z. M.; Su K. X. Advances in Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Catalytic Asymmetric Epoxidation. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 1603–1662. 10.1021/cr0406458. - DOI - PubMed
- Wang Ch.; Yamamoto H. Asymmetric Epoxidation Using Hydrogen Peroxide as Oxidant. Chem. - Asian J. 2015, 10, 2056–2068. 10.1002/asia.201500293. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Adam W.; Saha-Möller C. R.; Ganeshpure P. A. Synthetic Applications of Nonmetal Catalysts for Homogeneous Oxidations. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 3499–3548. 10.1021/cr000019k. - DOI - PubMed
- Kelly D. R.; Roberts S. M. Oligopeptides as catalysts for asymmetric epoxidation. Biopolymers 2006, 84, 74–89. 10.1002/bip.20373. - DOI - PubMed
- Wong O. A.; Shi Y. Organocatalytic Oxidation. Asymmetric Epoxidation of Olefins Catalyzed by Chiral Ketones and Iminium Salts. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 3958–3987. 10.1021/cr068367v. - DOI - PubMed
- Lattanzi A.Non-covalent Organocatalytic Approach in the Asymmetric Epoxidation of Electron-Poor Alkenes: Recent Developments Frontiers of Green Catalytic Selective Oxidations; Springer: Singapore, 2019.
- Triandafillidi I.; Tzaras D. I.; Kokotos Ch. G. Green Organocatalytic Oxidative Methods using Activated Ketones. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 2521–2535. 10.1002/cctc.201800013. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

