Amphiregulin retains ERα expression in acquired aromatase inhibitor resistant breast cancer cells
- PMID: 33112819
- PMCID: PMC7665895
- DOI: 10.1530/ERC-20-0258
Amphiregulin retains ERα expression in acquired aromatase inhibitor resistant breast cancer cells
Abstract
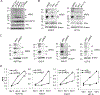
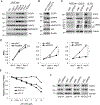
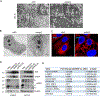
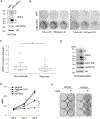
Acquired resistance to aromatase inhibitors (AIs) is a significant clinical issue in endocrine therapy for estrogen receptor (ER) positive breast cancer which accounts for the majority of breast cancer. Despite estrogen production being suppressed, ERα signaling remains active and plays a key role in most AI-resistant breast tumors. Here, we found that amphiregulin (AREG), an ERα transcriptional target and EGF receptor (EGFR) ligand, is crucial for maintaining ERα expression and signaling in acquired AI-resistant breast cancer cells. AREG was deregulated and critical for cell viability in ER+ AI-resistant breast cancer cells, and ectopic expression of AREG in hormone responsive breast cancer cells promoted endocrine resistance. RNA-sequencing and reverse phase protein array analyses revealed that AREG maintains ERα expression and signaling by activation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling and upregulation of forkhead box M1 (FOXM1) and serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase 3 (SGK3) expression. Our study uncovers a previously unappreciated role of AREG in maintaining ERα expression and signaling, and establishes the AREG-ERα crosstalk as a driver of acquired AI resistance in breast cancer.
Keywords: FOXM1; SGK3; endocrine resistance; estrogen receptor; mTOR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
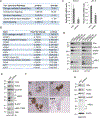
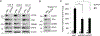
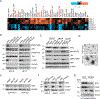
Similar articles
-
Mitochondrial stress adaptation promotes resistance to aromatase inhibitor in human breast cancer cells via ROS/calcium up-regulated amphiregulin-estrogen receptor loop signaling.Cancer Lett. 2021 Dec 28;523:82-99. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.09.043. Epub 2021 Oct 2. Cancer Lett. 2021. PMID: 34610415
-
SGK3 sustains ERα signaling and drives acquired aromatase inhibitor resistance through maintaining endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Feb 21;114(8):E1500-E1508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1612991114. Epub 2017 Feb 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28174265 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of anastrozole resistance in breast cancer: pivotal role of the Akt/mTOR pathway in the emergence of de novo or acquired resistance and importance of combining the allosteric Akt inhibitor MK-2206 with an aromatase inhibitor.Int J Cancer. 2013 Oct 1;133(7):1589-602. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28182. Epub 2013 May 2. Int J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23553037
-
An "omics" approach to determine the mechanisms of acquired aromatase inhibitor resistance.OMICS. 2011 Jun;15(6):347-52. doi: 10.1089/omi.2010.0097. Epub 2011 Feb 19. OMICS. 2011. PMID: 21332390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural and functional characterization of aromatase, estrogen receptor, and their genes in endocrine-responsive and -resistant breast cancer cells.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016 Jul;161:73-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2015.07.018. Epub 2015 Aug 13. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26277097 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Endocrine resistant breast cancer: brain metastasis.Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2022;3(2):240-251. doi: 10.37349/etat.2022.00081. Epub 2022 Apr 26. Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2022. PMID: 35505937 Free PMC article.
-
TXNIP Links Anticipatory Unfolded Protein Response to Estrogen Reprogramming Glucose Metabolism in Breast Cancer Cells.Endocrinology. 2022 Jan 1;163(1):bqab212. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqab212. Endocrinology. 2022. PMID: 34614512 Free PMC article.
-
New Promising Steroidal Aromatase Inhibitors with Multi-Target Action on Estrogen and Androgen Receptors for Breast Cancer Treatment.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jan 7;17(2):165. doi: 10.3390/cancers17020165. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39857947 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular features of luminal breast cancer defined through spatial and single-cell transcriptomics.Clin Transl Med. 2024 Jan;14(1):e1548. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1548. Clin Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38282415 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aggelis V & Johnston SRD 2019. Advances in Endocrine-Based Therapies for Estrogen Receptor-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer. Drugs 79 1849–1866. - PubMed
-
- Araki K & Miyoshi Y 2018. Mechanism of resistance to endocrine therapy in breast cancer: the important role of PI3K/Akt/mTOR in estrogen receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer 25 392–401. - PubMed
-
- Berasain C & Avila MA 2014. Amphiregulin. Semin Cell Dev Biol 28 31–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

