Prognostic role of gamma-glutamyl transferase in metastatic melanoma patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors
- PMID: 33113003
- PMCID: PMC10991606
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-020-02768-5
Prognostic role of gamma-glutamyl transferase in metastatic melanoma patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors
Abstract
Background: Hepatic immune-related adverse events (irAE) including elevated liver function tests (transaminases) occur in 1.4-22.3% of melanoma patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICPI) and constitute a potentially serious toxicity that is challenging to treat. In contrast to the liver transaminases alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), only little is known about the frequency and impact of gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) elevations.
Methods: GGT determined prior to and during therapy of metastatic melanoma patients treated with ICPI were retrospectively assessed in two independent cohorts (PD-1: n = 218, Ipi + Nivo: n = 148). Overall survival (OS) and best objective response were analyzed according to baseline and immune-related GGT (irGGT) elevations during treatment.
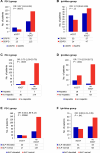
Results: In multivariate analysis, OS was reduced in patients with elevated baseline GGT (PD-1 group: hazard ratio [HR] 1.76, p = .0073; Ipi + Nivo group: HR 1.77, p = .032). Immune-related GGT elevation was recorded in 17% (PD-1 group) and 38.5% (Ipi + Nivo group). Of these patients, the majority (81 and 68%, respectively) had normal ALT and AST and showed no clinical signs of hepatotoxicity. Patients who experienced irGGT elevation had superior response (PD-1 group: odds ratio [OR] 3.57, p = .00072; Ipi + Nivo group: OR 1.74, p = .12) and OS (PD-1 group: HR 0.37, p = .0016; Ipi + Nivo group: HR 0.33, p = .00050).
Conclusions: The frequency of hepatic irAE is currently underestimated. The addition of the sensitive enzyme GGT to the laboratory panel before and during therapy with ICPI allows to detect two to three times more patients developing hepatic or hepatobiliary toxicity than known so far. Immune-related GGT elevations correlate with response and favorable survival. Precis for use in the Table of Contents The frequency of hepatotoxicity under immune checkpoint blockade is currently underestimated. We suggest the addition of gamma-glutamyl transferase to the laboratory panel in checkpoint inhibitor patients for the detection of hepatobiliary toxicity.
Keywords: Gamma-glutamyl transferase; Hepatotoxicity; Immune checkpoint inhibitors; Immune-related adverse events; Melanoma; PD-1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pooled Long-Term Outcomes With Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab or Nivolumab Alone in Patients With Advanced Melanoma.J Clin Oncol. 2025 Mar 10;43(8):938-948. doi: 10.1200/JCO.24.00400. Epub 2024 Nov 6. J Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39504507 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of BRAF mutation status on clinical outcomes with anti-PD-1 monotherapy versus combination ipilimumab/nivolumab in treatment-naïve advanced stage melanoma.Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2021 May;34(3):629-640. doi: 10.1111/pcmr.12944. Epub 2020 Nov 22. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2021. PMID: 33128316
-
Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab in Patients With Advanced Melanoma: Updated Survival, Response, and Safety Data in a Phase I Dose-Escalation Study.J Clin Oncol. 2018 Feb 1;36(4):391-398. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.72.2850. Epub 2017 Oct 17. J Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29040030 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluating the efficacy and safety of nivolumab and ipilimumab combination therapy compared to nivolumab monotherapy in advanced cancers (excluding melanoma): a systemic review and meta-analysis.J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2024 May 6;36(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s43046-024-00218-2. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2024. PMID: 38705953
-
Risks and benefits of reinduction ipilimumab/nivolumab in melanoma patients previously treated with ipilimumab/nivolumab.J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Oct;9(10):e003395. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-003395. J Immunother Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34702752 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Long-term survival following anti-PD-(L)1 monotherapy in advanced urothelial cancer and an assessment of potential prognostic clinical factors: a multicentre observational study.BJC Rep. 2024 Oct 23;2(1):84. doi: 10.1038/s44276-024-00104-3. BJC Rep. 2024. PMID: 39516359 Free PMC article.
-
γ-glutamyl transpeptidase-catalyzed polymer-enzyme-drug conjugate enhances penetration and suppression in oral squamous cell carcinoma via transdermal application.Mater Today Bio. 2025 Jun 13;33:101964. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101964. eCollection 2025 Aug. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40605992 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic potential of standard laboratory parameters in patients with metastatic renal cell cancer receiving first-line immunotherapy.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 25;14(1):25365. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76928-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39455722 Free PMC article.
-
Whole Exome Sequencing of Intracranial Epidermoid Cysts Reveals Immune-Associated Mechanistic and Potential Targets.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Oct 15;16(20):3487. doi: 10.3390/cancers16203487. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456581 Free PMC article.
-
Presence of autoantibodies in serum does not impact the occurrence of immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced hepatitis in a prospective cohort of cancer patients.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2022 Mar;148(3):647-656. doi: 10.1007/s00432-021-03870-6. Epub 2021 Dec 7. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34874490 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ribas A, Puzanov I, Dummer R, Schadendorf D, Hamid O, Robert C, et al. Pembrolizumab versus investigator-choice chemotherapy for ipilimumab-refractory melanoma (KEYNOTE-002): a randomised, controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:908–918. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00083-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

