Early Initiation of Extracorporeal Blood Purification Using the AN69ST (oXiris®) Hemofilter as a Treatment Modality for COVID-19 Patients: a Single-Centre Case Series
- PMID: 33113325
- PMCID: PMC8973137
- DOI: 10.21470/1678-9741-2020-0403
Early Initiation of Extracorporeal Blood Purification Using the AN69ST (oXiris®) Hemofilter as a Treatment Modality for COVID-19 Patients: a Single-Centre Case Series
Abstract
Introduction: Severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is characterised by hyperinflammatory state, systemic coagulopathies, and multiorgan involvement, especially acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). We here describe our preliminary clinical experience with COVID-19 patients treated via an early initiation of extracorporeal blood purification combined with systemic heparinisation and respiratory support.
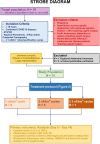
Methods: Fifteen patients were included; several biomarkers associated with COVID-19 severity were monitored. Personalised treatment was tailored according to the levels of interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8, tumour necrosis factor alpha, C-reactive protein (CRP), neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, thrombocyte counts, D-dimers, and fibrinogen. Treatment consisted of respiratory support, extracorporeal blood purification using the AN69ST (oXiris®) hemofilter, and 300 U/kg heparin to maintain activation clotting time ≥ 180 seconds.
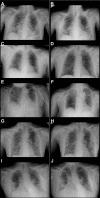
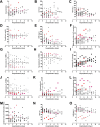
Results: Ten patients presented with severe to critical disease (dyspnoea, hypoxia, respiratory rate > 30/min, peripheral oxygen saturation < 90%, or > 50% lung involvement on X-ray imaging). The median intensive care unit length of stay was 9.3 days (interquartile range 5.3-10.1); two patients developed ARDS and died after 5 and 26 days. Clinical improvement was associated with normalisation (increase) of thrombocytes and white blood cells, stable levels of IL-6 (< 50 ng/mL), and a decrease of CRP and fibrinogen.
Conclusion: Continuous monitoring of COVID-19 severity biomarkers and radiological imaging is crucial to assess disease progression, uncontrolled inflammation, and to avert irreversible multiorgan failure. The combination of systemic heparin anticoagulation regimens and extracorporeal blood purification using cytokine-adsorbing hemofilters may reduce hyperinflammation, prevent coagulopathy, and support clinical recovery.
Keywords: Blood Platets; C-Reactive Protein; COVID-19; Cytokines; Heparin; Interleukin-6; Respiratory Distress Syndrome, Adult; Respiratory Rate; TNF protein, human; Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

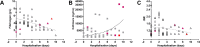


Similar articles
-
Extracorporeal Blood Purification in Moderate and Severe COVID-19 Patients: A Prospective Cohort Study.Blood Purif. 2022;51(3):233-242. doi: 10.1159/000515627. Epub 2021 Jun 14. Blood Purif. 2022. PMID: 34126617 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The CHARTER-Ireland trial: can nebulised heparin reduce acute lung injury in patients with SARS-CoV-2 requiring advanced respiratory support in Ireland: a study protocol and statistical analysis plan for a randomised control trial.Trials. 2022 Sep 14;23(1):774. doi: 10.1186/s13063-022-06518-z. Trials. 2022. PMID: 36104785 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells derived from perinatal tissues for treatment of critically ill COVID-19-induced ARDS patients: a case series.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Jan 29;12(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02165-4. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 33514427 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Tocilizumab for the treatment of severe COVID-19 pneumonia with hyperinflammatory syndrome and acute respiratory failure: A single center study of 100 patients in Brescia, Italy.Autoimmun Rev. 2020 Jul;19(7):102568. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102568. Epub 2020 May 3. Autoimmun Rev. 2020. PMID: 32376398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathomechanisms Underlying Hypoxemia in Two COVID-19-Associated Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Phenotypes: Insights From Thrombosis and Hemostasis.Shock. 2022 Jan 1;57(1):1-6. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000001825. Shock. 2022. PMID: 34172612 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Extracorporeal blood purification strategies in sepsis and septic shock: An insight into recent advancements.World J Crit Care Med. 2023 Mar 9;12(2):71-88. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v12.i2.71. eCollection 2023 Mar 9. World J Crit Care Med. 2023. PMID: 37034019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy with the oXiris Hemofilter on Critically Ill Patients: A Narrative Review.J Clin Med. 2022 Nov 13;11(22):6719. doi: 10.3390/jcm11226719. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36431196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute Kidney Injury and Blood Purification Techniques in Severe COVID-19 Patients.J Clin Med. 2022 Oct 25;11(21):6286. doi: 10.3390/jcm11216286. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36362514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of short-wave diathermy treatment for moderate COVID-19 patients: a prospective, double-blind, randomized controlled clinical study.Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2022 Feb;58(1):137-143. doi: 10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06892-1. Epub 2021 May 27. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2022. PMID: 34042412 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Hemoperfusion and blood purification strategies in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review.Artif Organs. 2021 Dec;45(12):1466-1476. doi: 10.1111/aor.14078. Epub 2021 Oct 10. Artif Organs. 2021. PMID: 34632596 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhou F, Yu T, Du R, Fan G, Liu Y, Liu Z, et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020;395(10229):1054–1062. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3. Erratum in: Lancet. 2020;395(10229):1038. Erratum in: Lancet. 2020;395(10229):1038. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
