Sox2 and Canonical Wnt Signaling Interact to Activate a Developmental Checkpoint Coordinating Morphogenesis with Mesoderm Fate Acquisition
- PMID: 33113369
- PMCID: PMC7653682
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108311
Sox2 and Canonical Wnt Signaling Interact to Activate a Developmental Checkpoint Coordinating Morphogenesis with Mesoderm Fate Acquisition
Abstract
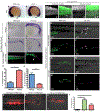
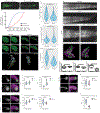
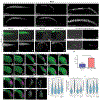
Animal embryogenesis requires a precise coordination between morphogenesis and cell fate specification. During mesoderm induction, mesodermal fate acquisition is tightly coordinated with the morphogenetic process of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). In zebrafish, cells exist transiently in a partial EMT state during mesoderm induction. Here, we show that cells expressing the transcription factor Sox2 are held in the partial EMT state, stopping them from completing the EMT and joining the mesoderm. This is critical for preventing the formation of ectopic neural tissue. The mechanism involves synergy between Sox2 and the mesoderm-inducing canonical Wnt signaling pathway. When Wnt signaling is inhibited in Sox2-expressing cells trapped in the partial EMT, cells exit into the mesodermal territory but form an ectopic spinal cord instead of mesoderm. Our work identifies a critical developmental checkpoint that ensures that morphogenetic movements establishing the mesodermal germ layer are accompanied by robust mesodermal cell fate acquisition.
Keywords: canonical Wnt signaling; mesoderm; neuromesodermal progenitors; somite; sox2; spinal cord; tbx16; zebrafish.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Blader P, Plessy C, and Strähle U (2003). Multiple regulatory elements with spatially and temporally distinct activities control neurogenin1 expression in primary neurons of the zebrafish embryo. Mech. Dev 120, 211–218. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

