One-step rapid quantification of SARS-CoV-2 virus particles via low-cost nanoplasmonic sensors in generic microplate reader and point-of-care device
- PMID: 33113383
- PMCID: PMC7557276
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112685
One-step rapid quantification of SARS-CoV-2 virus particles via low-cost nanoplasmonic sensors in generic microplate reader and point-of-care device
Abstract
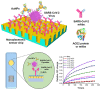
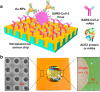
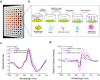
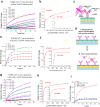
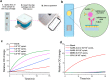
The spread of SARS-CoV-2 virus in the ongoing global pandemic has led to infections of millions of people and losses of many lives. The rapid, accurate and convenient SARS-CoV-2 virus detection is crucial for controlling and stopping the pandemic. Diagnosis of patients in the early stage infection are so far limited to viral nucleic acid or antigen detection in human nasopharyngeal swab or saliva samples. Here we developed a method for rapid and direct optical measurement of SARS-CoV-2 virus particles in one step nearly without any sample preparation using a spike protein specific nanoplasmonic resonance sensor. As low as 370 vp/mL were detected in one step within 15 min and the virus concentration can be quantified linearly in the range of 0 to 107 vp/mL. Measurements shown on both generic microplate reader and a handheld smartphone connected device suggest that our low-cost and rapid detection method may be adopted quickly under both regular clinical environment and resource-limited settings.
Keywords: Antibody conjugation; COVID-19; Nanoplasmonic sensor; Point of care testing; SARS-CoV-2 virus.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Ai J.-W., Zhang H.-C., Xu T., Wu J., Zhu M., Yu Y.-Q., Zhang H.-Y., Shen Z., Li Y., Zhou X., Zang G.-Q., Xu J., Chen W.-J., Li Y.-J., Xie D.-S., Zhou M.-Z., Sun J.-Y., Chen J.-Z., Zhang W.-H. Optimizing diagnostic strategy for novel coronavirus pneumonia, a multi-center study in Eastern China. medRxiv. 2020;2020 2002.2013.20022673.
-
- Baek Y.H., Um J., Antigua K.J.C., Park J.H., Kim Y., Oh S., Kim Y.I., Choi W.S., Kim S.G., Jeong J.H., Chin B.S., Nicolas H.D.G., Ahn J.Y., Shin K.S., Choi Y.K., Park J.S., Song M.S. Development of a reverse transcription-loop-mediated isothermal amplification as a rapid early-detection method for novel SARS-CoV-2. Emerg. Microb. Infect. 2020;9(1):998–1007. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belushkin A., Yesilkoy F., Altug H. Nanoparticle-enhanced plasmonic biosensor for digital biomarker detection in a microarray. ACS Nano. 2018;12(5):4453–4461. - PubMed
-
- Chang Y.F., Wang W.H., Hong Y.W., Yuan R.Y., Chen K.H., Huang Y.W., Lu P.L., Chen Y.H., Chen Y.A., Su L.C., Wang S.F. Simple strategy for rapid and sensitive detection of avian influenza A H7N9 virus based on intensity-modulated SPR biosensor and new generated antibody. Anal. Chem. 2018;90(3):1861–1869. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

