Taxonomy and Phylogenetic Research on Ralstonia solanacearum Species Complex: A Complex Pathogen with Extraordinary Economic Consequences
- PMID: 33113847
- PMCID: PMC7694096
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens9110886
Taxonomy and Phylogenetic Research on Ralstonia solanacearum Species Complex: A Complex Pathogen with Extraordinary Economic Consequences
Abstract
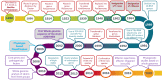
The bacterial wilt pathogen, first known as Bacillus solanacearum, has undergone numerous taxonomic changes since its first description in 1896. The history and significance of this pathogen is covered in this review with an emphasis on the advances in technology that were used to support each reclassification that finally led to the current separation of Ralstonia solanacearum into three genomic species. Frequent name changes occurred as methodology transitioned from phenotypic, biochemical, and molecular studies, to genomics and functional genomics. The diversity, wide host range, and geographical distribution of the bacterial wilt pathogen resulted in its division into three species as genomic analyses elucidated phylogenetic relationships among strains. Current advances in phylogenetics and functional genomics now open new avenues for research into epidemiology and control of the devastating bacterial wilt disease.
Keywords: Bugtok disease; Granville Wilt of tobacco; Ralstonia solanacearum species complex; bacterial wilt; brown rot of potato; moko disease of banana; phylogenomic; plant bacteria; taxonomy; tomato wilt.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Ralstonia solanacearum, a widespread bacterial plant pathogen in the post-genomic era.Mol Plant Pathol. 2013 Sep;14(7):651-62. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12038. Epub 2013 May 30. Mol Plant Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23718203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The in planta transcriptome of Ralstonia solanacearum: conserved physiological and virulence strategies during bacterial wilt of tomato.mBio. 2012 Aug 31;3(4):e00114-12. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00114-12. Print 2012. mBio. 2012. PMID: 22807564 Free PMC article.
-
Genomes of three tomato pathogens within the Ralstonia solanacearum species complex reveal significant evolutionary divergence.BMC Genomics. 2010 Jun 15;11:379. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-379. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20550686 Free PMC article.
-
Ralstonia solanacearum: secrets of a major pathogen unveiled by analysis of its genome.Mol Plant Pathol. 2002 May 1;3(3):111-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1364-3703.2002.00102.x. Mol Plant Pathol. 2002. PMID: 20569316
-
Bacterial Diseases of Bananas and Enset: Current State of Knowledge and Integrated Approaches Toward Sustainable Management.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Jul 20;8:1290. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01290. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28785275 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biocontrol Potential of Chitin and Chitosan Extracted from Black Soldier Fly Pupal Exuviae against Bacterial Wilt of Tomato.Microorganisms. 2022 Jan 13;10(1):165. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10010165. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35056613 Free PMC article.
-
Stability analysis of reference genes for RT-qPCR assays involving compatible and incompatible Ralstonia solanacearum-tomato 'Hawaii 7996' interactions.Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 21;11(1):18719. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-97854-8. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34548514 Free PMC article.
-
An ancient cis-element targeted by Ralstonia solanacearum TALE-like effectors facilitates the development of a promoter trap that could confer broad-spectrum wilt resistance.Plant Biotechnol J. 2024 Mar;22(3):602-616. doi: 10.1111/pbi.14208. Epub 2023 Oct 23. Plant Biotechnol J. 2024. PMID: 37870975 Free PMC article.
-
Ralstonia solanacearum - A soil borne hidden enemy of plants: Research development in management strategies, their action mechanism and challenges.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Feb 24;14:1141902. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1141902. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 36909396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant and soil-associated microbiome dynamics determine the fate of bacterial wilt pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum.Planta. 2023 Aug 1;258(3):57. doi: 10.1007/s00425-023-04209-w. Planta. 2023. PMID: 37524889 Review.
References
-
- Kannan V., Bastas K., Antony R. Sustainable Approaches to Controlling Plant Pathogenic Bacteria. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2015. Plant pathogenic bacteria: An overview; pp. 1–16.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

