Anti-Angiogenic Properties of Ginsenoside Rg3
- PMID: 33113992
- PMCID: PMC7660320
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25214905
Anti-Angiogenic Properties of Ginsenoside Rg3
Abstract
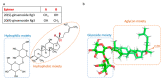
Ginsenoside Rg3 (Rg3) is a member of the ginsenoside family of chemicals extracted from Panax ginseng. Like other ginsenosides, Rg3 has two epimers: 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 (SRg3) and 20(R)-ginsenoside Rg3 (RRg3). Rg3 is an intriguing molecule due to its anti-cancer properties. One facet of the anti-cancer properties of Rg3 is the anti-angiogenic action. This review describes the controversies on the effects and effective dose range of Rg3, summarizes the evidence on the efficacy of Rg3 on angiogenesis, and raises the possibility that Rg3 is a prodrug.
Keywords: 20(R)-ginsenoside Rg3; 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3; angiogenesis; epimer; ginsenoside Rg3.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The angiosuppressive effects of 20(R)- ginsenoside Rg3.Biochem Pharmacol. 2006 Aug 14;72(4):437-45. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.04.034. Epub 2006 May 12. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16793023
-
Ginsenoside Rg3 attenuates tumor angiogenesis via inhibiting bioactivities of endothelial progenitor cells.Cancer Biol Ther. 2012 May;13(7):504-15. doi: 10.4161/cbt.19599. Epub 2012 May 1. Cancer Biol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22406998
-
20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 enhances glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and activates AMPK.Biol Pharm Bull. 2008 Apr;31(4):748-51. doi: 10.1248/bpb.31.748. Biol Pharm Bull. 2008. PMID: 18379076
-
Insights into the antitumor mechanism of ginsenosides Rg3.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Mar;48(3):2639-2652. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06187-2. Epub 2021 Mar 4. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33661439 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms behind the inhibitory effects of ginsenoside Rg3 on hepatic fibrosis: a review.Arch Toxicol. 2025 Feb;99(2):541-561. doi: 10.1007/s00204-024-03941-w. Epub 2024 Dec 27. Arch Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39729114 Review.
Cited by
-
Harnessing Jasmonate Pathways: PgJAR1's Impact on Ginsenoside Accumulation in Ginseng.Plants (Basel). 2025 Mar 8;14(6):847. doi: 10.3390/plants14060847. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40265796 Free PMC article.
-
Examination of Combined Treatment of Ginsenoside Rg3 and 5-Fluorouracil in Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Jun 28;2022:2813142. doi: 10.1155/2022/2813142. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. PMID: 35799655 Free PMC article.
-
Ginsenoside Rg3 induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation by down-regulating TIGAR in rats with gastric precancerous lesions.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 Jul 15;22(1):188. doi: 10.1186/s12906-022-03669-z. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 35840932 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-leukemia effects of ginsenoside monomer: A narrative review of pharmacodynamics study.Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2024 Feb 25;100:100739. doi: 10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100739. eCollection 2024. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2024. PMID: 38706463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transformation of Ginsenosides by Lactiplantibacillus plantarum MB11 Fermentation: Minor Ginsenosides Conversion and Enhancement of Anti-Colorectal Cancer Activity.Molecules. 2023 Dec 20;29(1):27. doi: 10.3390/molecules29010027. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38202610 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jo S.K., Kim I.S., Yoon K.S., Yoon H.H., Yoo H.H. Preparation of ginsenosides Rg3, Rk1, and Rg5-selectively enriched ginsengs by a simple steaming process. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015;240:251–256. doi: 10.1007/s00217-014-2370-1. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

