Molecular Control and Application of Male Fertility for Two-Line Hybrid Rice Breeding
- PMID: 33114094
- PMCID: PMC7660317
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21217868
Molecular Control and Application of Male Fertility for Two-Line Hybrid Rice Breeding
Abstract
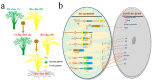
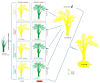
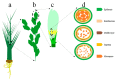
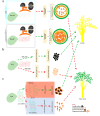
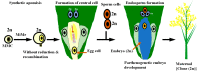
The significance of the climate change may involve enhancement of plant growth as well as utilization of the environmental alterations in male fertility (MF) regulation via male sterility (MS) systems. We described that MS systems provide a fundamental platform for improvement in agriculture production and have been explicated for creating bulk germplasm of the two-line hybrids (EGMS) in rice as compared to the three-line, to gain production sustainability and exploit its immense potential. Environmental alterations such as photoperiod and/or temperature and humidity regulate MS in EGMS lines via genetic and epigenetic changes, regulation of the noncoding RNAs, and RNA-metabolism including the transcriptional factors (TFs) implication. Herein, this article enlightens a deep understanding of the molecular control of MF in EGMS lines and exploring the regulatory driving forces that function efficiently during plant adaption under a changing environment. We highlighted a possible solution in obtaining more stable hybrids through apomixis (single-line system) for seed production.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; EGMS; HGMS; PGMS; PTGMS; TGMS; apomixes; hybrid rice; male fertility or sterility; single-line; three-line; two-line.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Palanisamy D., Marappan S., Ponnuswamy R.D., Mahalingam P.S., Bohar R., Vaidyanathan S. Accelerating hybrid rice breeding through the adoption of doubled haploid technology for R-line development. Biologia. 2019;74:1259–1269. doi: 10.2478/s11756-019-00300-4. - DOI
-
- Khush G.S. Strategies for increasing the yield potential of cereals: Case of rice as an example. Plant Breed. 2013;132:433–436. doi: 10.1111/pbr.1991. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Grant No. 2016YFD0100400/The National Key Research and Development Program of China
- Grant No. 31921004, 31571255, 31871700/The National Natural Science Foundation of China
- Grant No. 2017A030306001/The Guangdong Natural Science Funds for Distinguished Young Scholars
- Grant No. 201710010106/The Pearl River S&T Nova Program of Guangzhou
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

