Rare Primary Malignant Bone Sarcomas
- PMID: 33114111
- PMCID: PMC7690832
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12113092
Rare Primary Malignant Bone Sarcomas
Abstract
Rare primary malignant bone sarcomas (RPMBS), other than osteosarcoma, chondrosarcoma, chordoma, and Ewing sarcoma, account for about 5-10% of primary bone tumors and represent a major diagnostic challenge. These tumors include spindle cell and round cell sarcoma entities, hemangiopericytoma-like and vascular tumors. Additionally, several histotypes, traditionally described in the soft tissues, such as myxofibrosarcoma, synovial sarcoma, and malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor of bone, have been reported in patients with primary bone tumors. While wide surgical resection is the mainstay of local treatment, systemic therapy of these rare entities is controversial. Patients with undifferentiated spindle cell or pleomorphic high-grade tumors of bone, are usually treated with osteosarcoma-like chemotherapy, while patients with round cell and undifferentiated round cell tumors (URCTs), may respond to sarcoma treatment regimens for Ewing sarcoma patients. Studies on analogies and differences among these ultra-rare tumors have seldom been reported. This review describes relevance, clinical aspects, diagnostic procedures, staging, treatment recommendations, and current research in this composite tumor group.
Keywords: BCOR-CCNH3; CIC-DUX4; bone tumor; chemotherapy; molecular diagnostic; rare tumor; round cells sarcoma; sarcoma; spindle cells sarcoma; vascular sarcoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
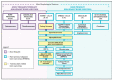
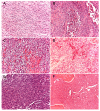
References
-
- SEER Cancer Statistics Factsheets: Bone and Joint Cancer. National Cancer Institute; Bethesda, MD, USA: 2016. [(accessed on 22 April 2016)]. Available online: http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/bones.html.
-
- Romeo S., Boveé J.V., Kroon H.M., Tirabosco R., Natali C., Zanatta L., Sciot R., Mertens F., Athanasou N., Alberghini M., et al. Malignant fibrous histiocytoma and fibrosarcoma of bone: A re-assessment in the light of currently employed morphological, immunohistochemical and molecular approaches. Virchows Arch. 2012;461:561–570. doi: 10.1007/s00428-012-1306-z. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

