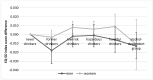
The Association between Alcohol Drinking Patterns and Health-Related Quality of Life in the Korean Adult Population: Effects of Misclassification Error on Estimation of Association
- PMID: 33114114
- PMCID: PMC7660298
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17217758
The Association between Alcohol Drinking Patterns and Health-Related Quality of Life in the Korean Adult Population: Effects of Misclassification Error on Estimation of Association
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to investigate the association between drinking patterns and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in the Korean general population and to validate the estimation of the association of alcohol use on HRQoL when former drinkers are separated from never drinkers and low-risk drinkers depending on gender. Data were collected from 23,055 adults (over 19 years old) who completed the Korean National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey (2010-2013). Multivariate logistic and linear regression analyses were performed to investigate the association between drinking patterns and HRQoL. When former drinkers were separated from never drinkers and low-risk drinkers to control for misclassification bias, there were gender differences in the associations between alcohol use and HRQoL. Although the estimation of the association of alcohol use was not valid in men, the estimation of association was valid in women, as low-risk women drinkers showed better HRQoL than nondrinkers. Therefore, when conducting research related to alcohol and health, analyses should correct for the various confounding variables and minimize the misclassification bias of drinking patterns. It is also necessary to consider gender characteristics when intervening to improve HRQoL related to drinking.
Keywords: AUDIT; alcohol drinking; gender; quality of life.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between alcohol consumption and periodontal disease: the 2008 to 2010 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.J Periodontol. 2014 Nov;85(11):1521-8. doi: 10.1902/jop.2014.130782. Epub 2014 Jul 10. J Periodontol. 2014. PMID: 25008215
-
The association between alcohol consumption patterns and health-related quality of life in a nationally representative sample of South Korean adults.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 18;10(3):e0119245. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119245. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25786249 Free PMC article.
-
Association between alcohol consumption and bone mineral density in elderly Korean men and women.Arch Osteoporos. 2018 Apr 25;13(1):46. doi: 10.1007/s11657-018-0462-4. Arch Osteoporos. 2018. PMID: 29696513
-
Association of Alcohol Drinking Patterns with Metabolic Syndrome and Its Components in Korean Adults: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2016-2018.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Jun 14;18(12):6433. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18126433. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34198573 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between Gender, Alcohol Use and Negative Consequences among Korean College Students: A National Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Jul 18;17(14):5192. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17145192. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32708392 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association between Alcohol Consumption and Health-Related Quality of Life among Hospital and Ambulatory Care Patients with Past Year Depressive Symptoms.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Nov 8;19(22):14664. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192214664. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36429382 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Middle-Aged Women's Demographics, Health Behavior, And Health Status on Health-Related Quality of Life by Economic Activity Participation: Panel Evidence from Korea.Iran J Public Health. 2024 Apr;53(4):809-817. doi: 10.18502/ijph.v53i4.15557. Iran J Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39444464 Free PMC article.
-
Perceived social measures and drinking behavior during the COVID-19 pandemic in Thailand.J Public Health Policy. 2024 Dec;45(4):700-713. doi: 10.1057/s41271-024-00521-1. Epub 2024 Sep 18. J Public Health Policy. 2024. PMID: 39294344 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization Global Status Report on Alcohol and Health 2018. [(accessed on 26 October 2018)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/substance_abuse/publications/global_alcohol_report/g...
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical