Differential Gene Expression in Brain and Liver Tissue of Wistar Rats after Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Deprivation
- PMID: 33114225
- PMCID: PMC7711450
- DOI: 10.3390/clockssleep2040033
Differential Gene Expression in Brain and Liver Tissue of Wistar Rats after Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Deprivation
Abstract
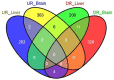
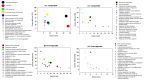
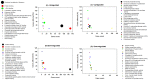
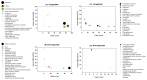
Sleep is essential for the survival of most living beings. Numerous researchers have identified a series of genes that are thought to regulate "sleep-state" or the "deprived state". As sleep has a significant effect on physiology, we believe that lack of total sleep, or particularly rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, for a prolonged period would have a profound impact on various body tissues. Therefore, using the microarray method, we sought to determine which genes and processes are affected in the brain and liver of rats following nine days of REM sleep deprivation. Our findings showed that REM sleep deprivation affected a total of 652 genes in the brain and 426 genes in the liver. Only 23 genes were affected commonly, 10 oppositely, and 13 similarly across brain and liver tissue. Our results suggest that nine-day REM sleep deprivation differentially affects genes and processes in the brain and liver of rats.
Keywords: differential gene expression in brain and liver tissue; microarray analysis; rapid eye movement sleep deprivation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest and all funding and scientific contributions are fully recognized.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effect of rapid eye movement sleep deprivation on rat brain monoamine oxidases.Neuroscience. 1993 Aug;55(3):677-83. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90433-g. Neuroscience. 1993. PMID: 8413930
-
Rapid eye movement (rem) sleep deprivation: effect on acid mucopolysaccharides in rat brain.Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1975 May;83(2):221-32. doi: 10.3109/13813457509081866. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1975. PMID: 54054
-
Rapid eye movement sleep deprivation induces an increase in acetylcholinesterase activity in discrete rat brain regions.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2001 Jan;34(1):103-9. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x2001000100012. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2001. PMID: 11151034
-
Rapid Eye Movement sleep deprivation of rat generates ROS in the hepatocytes and makes them more susceptible to oxidative stress.Sleep Sci. 2018 Jul-Aug;11(4):245-253. doi: 10.5935/1984-0063.20180039. Sleep Sci. 2018. PMID: 30746042 Free PMC article.
-
Cytomorphometric changes in rat brain neurons after rapid eye movement sleep deprivation.Neuroscience. 2005;135(3):679-90. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.06.085. Epub 2005 Sep 8. Neuroscience. 2005. PMID: 16154283
Cited by
-
Recovery Sleep Immediately after Prolonged Sleep Deprivation Stimulates the Transcription of Integrated Stress Response-Related Genes in the Liver of Male Rats.Clocks Sleep. 2022 Nov 9;4(4):623-632. doi: 10.3390/clockssleep4040048. Clocks Sleep. 2022. PMID: 36412581 Free PMC article.
-
The Genetic Basis of Probable REM Sleep Behavior Disorder in Parkinson's Disease.Brain Sci. 2023 Jul 30;13(8):1146. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13081146. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37626502 Free PMC article.
-
Chronodisruption and Gut Microbiota: Triggering Glycemic Imbalance in People with Type 2 Diabetes.Nutrients. 2024 Feb 23;16(5):616. doi: 10.3390/nu16050616. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38474745 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

