Polydeoxyribonucleotide Exerts Protective Effect Against CCl4-Induced Acute Liver Injury Through Inactivation of NF-κB/MAPK Signaling Pathway in Mice
- PMID: 33114315
- PMCID: PMC7660684
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21217894
Polydeoxyribonucleotide Exerts Protective Effect Against CCl4-Induced Acute Liver Injury Through Inactivation of NF-κB/MAPK Signaling Pathway in Mice
Abstract
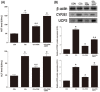
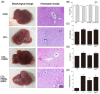
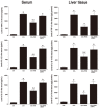
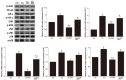
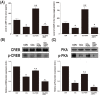
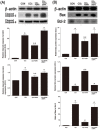
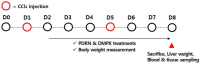
Acute liver injury (ALI) causes life-threatening clinical problem, and its underlying etiology includes inflammation and apoptosis. An adenosine A2A receptor agonist, polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN), exhibits anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects by inhibiting the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines. In the current study, the protective effect of PDRN against carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced ALI was investigated using mice. For the induction of ALI, mice received intraperitoneal injection of CCl4 twice over seven days. Mice from the PDRN-treated groups received an intraperitoneal injection of 200 μL saline containing PDRN (8 mg/kg), once a day for seven days, starting on day 1 after the first CCl4 injection. In order to confirm that the action of PDRN occurs through the adenosine A2A receptor, 8 mg/kg 3,7-dimethyl-1-propargylxanthine (DMPX), an adenosine A2A receptor antagonist, was treated with PDRN. Administration of CCl4 impaired liver tissue and increased the liver index and histopathologic score. The expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines was increased, and apoptosis was induced by the administration of CCl4. Administration of CCl4 activated nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) and facilitated phosphorylation of signaling factors in mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). In contrast, PDRN treatment suppressed the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines and inhibited apoptosis. PDRN treatment inactivated NF-κB and suppressed phosphorylation of signaling factors in MAPK. As a result, liver index and histopathologic score were reduced by PDRN treatment. When PDRN was treated with DMPX, the anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effect of PDRN disappeared. Therefore, PDRN can be used as an effective therapeutic agent for acute liver damage.
Keywords: acute liver injury; apoptosis; inflammation; mitogen-activated protein kinase; nuclear factor-kappa B; polydeoxyribonucleotide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

