Innovative Extraction Techniques Using Deep Eutectic Solvents and Analytical Methods for the Isolation and Characterization of Natural Bioactive Compounds from Plant Material
- PMID: 33114332
- PMCID: PMC7690858
- DOI: 10.3390/plants9111428
Innovative Extraction Techniques Using Deep Eutectic Solvents and Analytical Methods for the Isolation and Characterization of Natural Bioactive Compounds from Plant Material
Abstract
The growing interest of the food, pharmaceutical and cosmetics industries in naturally occurring bioactive compounds or secondary plant metabolites also leads to a growing demand for the development of new and more effective analysis and isolation techniques. The extraction of bioactive compounds from plant material has always been a challenge, accompanied by increasingly strict control requirements for the final products and a growing interest in environmental protection. However, great efforts have been made in this direction and today a considerable number of innovative extraction techniques have been developed using green, environmentally friendly solvents. These solvents include the deep eutectic solvents (DES) and their natural equivalents, the natural deep eutectic solvents (NADES). Due to their adjustable physical-chemical properties and their green character, it is expected that DES/NADES could be the most widely used solvents in the future, not only in extraction processes but also in other research areas such as catalysis, electrochemistry or organic synthesis. Consequently, this review provided an up-to-date systematic overview of the use of DES/NADES in combination with innovative extraction techniques for the isolation of bioactive compounds from various plant materials. The topicality of the field was confirmed by a detailed search on the platform WoS (Web of Science), which resulted in more than 100 original research papers on DES/NADES for bioactive compounds in the last three years. Besides the isolation of bioactive compounds from plants, different analytical methods are presented and discussed.
Keywords: analytical methods; bioactive compounds; deep eutectic solvents (DES); innovative extraction techniques; microwave-assisted extraction (MAE); natural deep eutectic solvents (NADES); plant material; ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
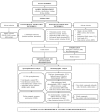
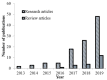
References
-
- Sahebi M., Hanafi M.M., van Wijnen A.J., Akmar A.S.N., Azizi P., Idris A.S., Taheri S., Foroughi M. Profiling secondary metabolites of plant defence mechanisms and oil palm in response to Ganoderma boninense attack. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegradation. 2017;122:151–164. doi: 10.1016/j.ibiod.2017.04.016. - DOI
-
- Choi Y.H., Verpoorte R. Green solvents for the extraction of bioactive compounds from natural products using ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2019;26:87–93. doi: 10.1016/j.cofs.2019.04.003. - DOI
-
- Gałuszka A., Migaszewski Z., Namieśnik J. The 12 principles of green analytical chemistry and the SIGNIFICANCE mnemonic of green analytical practices. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013;50:78–84. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2013.04.010. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

