Recent Progress in Conducting Polymers for Hydrogen Storage and Fuel Cell Applications
- PMID: 33114547
- PMCID: PMC7693427
- DOI: 10.3390/polym12112480
Recent Progress in Conducting Polymers for Hydrogen Storage and Fuel Cell Applications
Abstract
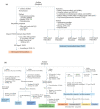
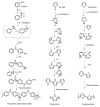
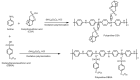
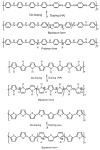
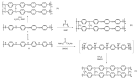
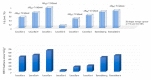
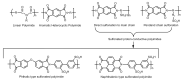
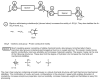
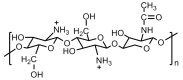
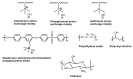
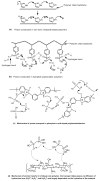
Hydrogen is a clean fuel and an abundant renewable energy resource. In recent years, huge scientific attention has been invested to invent suitable materials for its safe storage. Conducting polymers has been extensively investigated as a potential hydrogen storage and fuel cell membrane due to the low cost, ease of synthesis and processability to achieve the desired morphological and microstructural architecture, ease of doping and composite formation, chemical stability and functional properties. The review presents the recent progress in the direction of material selection, modification to achieve appropriate morphology and adsorbent properties, chemical and thermal stabilities. Polyaniline is the most explored material for hydrogen storage. Polypyrrole and polythiophene has also been explored to some extent. Activated carbons derived from conducting polymers have shown the highest specific surface area and significant storage. This review also covers recent advances in the field of proton conducting solid polymer electrolyte membranes in fuel cells application. This review focuses on the basic structure, synthesis and working mechanisms of the polymer materials and critically discusses their relative merits.
Keywords: conducting polymers; fuel cell; hydrogen storage; polyaniline; polypyrrole; polythiophene; proton conducting solid polymer electrolytes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


















References
-
- Attia N.F., Lee S.M., Kim H.J., Geckeler K.E. Nanoporous polypyrrole: Preparation and hydrogen storage properties. Int. J. Energy Res. 2014;38:466–476. doi: 10.1002/er.3095. - DOI
-
- Hardy B., Tamburello D., Corgnale C. Hydrogen storage adsorbent systems acceptability envelope. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 2018;43:19528–19539. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.08.140. - DOI
-
- Bae C. Development of Novel Proton-Conductive Polymers for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC) Technology 2007. 7,615,300. U.S. Patent. 2009 Nov 10;
-
- Prater K. The renaissance of the solid polymer fuel cell. J. Power Sources. 1990;29:239–250. doi: 10.1016/0378-7753(90)80023-7. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

