Impact of Surface Treatment on the Functional Properties Stainless Steel for Biomedical Applications
- PMID: 33114559
- PMCID: PMC7662572
- DOI: 10.3390/ma13214767
Impact of Surface Treatment on the Functional Properties Stainless Steel for Biomedical Applications
Abstract
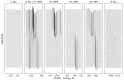
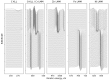
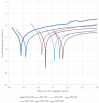
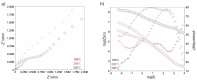
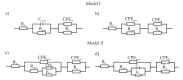
The main goal of the carried out tests was to analyze the influence of the surface modification of a substrate by depositing composite ZnO layers by the Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) method. The samples were subjected to preliminary surface modification consisting of being sandblasted and electropolished. A ZnO layer was applied to the prepared substrates by the ALD method. As a precursor of ZnO, diethylzinc (DEZ) was used, which reacted with water, enabling the deposition of the thin films. The chamber temperature was as follows: T = 100-300 °C. The number of cycles was 500 and 1500. As part of the assessment of the physicochemical properties of the resulting surface layers, the tests of chemical composition of the layer, pitting corrosion, impedance corrosion, adhesion to the metal substrate, morphology surface, and wettability were carried out. On the basis of the obtained research, it was found that a composite ZnO layer deposited onto a substrate previously subjected to the electrochemical polishing process has more favorable physicochemical properties. Moreover, an influence of temperature and the number of cycles of the deposition process on the obtained properties was observed, where the ZnO layer was characterized by more favorable properties at a temperature of 200-300 °C at 1500 cycles of the deposition process.
Keywords: 316LVM steel; ALD method; ZnO layer; electropolised; sandblasted.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures













References
-
- El Hadad A.A., García-Galván F.R., Mezour M.A., Hickman G.J., Soliman I.E., Jiménez-Morales A., Barranco V., Galván J.C., Perry C.C. Organic-inorganic hybrid coatings containing phosphorus precursors prepared by sol–gel on Ti6Al4V alloy: Electrochemical and in-vitro biocompatibility evaluation. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020;148:105834. doi: 10.1016/j.porgcoat.2020.105834. - DOI
-
- Yu S., Li Z., Han L., Zhao Y., Fu T. Biocompatible MgO Film on Titanium Substrate Prepared by Sol-gel Method. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2018;47:2663–2667.
-
- Salimon I., Temirov A., Kubasov I., Skryleva E., Kislyuk A., Turutin A., Kiselev D., Ilina T., Zhukov R., Statnik E., et al. Characterization of Si-DLC films synthesized by low cost plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Mater. Today Proc. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.06.379. In press. - DOI
-
- Song C., Liu M., Deng Z., Niu S., Deng C., Liao H. A novel method for in-situ synthesized TiN coatings by plasma spray-physical vapor deposition. Mater. Lett. 2018;217:127–130. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2018.01.068. - DOI
-
- Basiaga M., Walke W., Staszuk M., Kajzer W., Kajzer A., Nowińska K. Influence of ALD process parameters on the physical and chemical properties of the surface of vascular stents. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2017;17:32–42. doi: 10.1016/j.acme.2016.08.001. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

