Immersive Virtual Environments and Wearable Haptic Devices in rehabilitation of children with neuromotor impairments: a single-blind randomized controlled crossover pilot study
- PMID: 33115487
- PMCID: PMC7594483
- DOI: 10.1186/s12984-020-00771-6
Immersive Virtual Environments and Wearable Haptic Devices in rehabilitation of children with neuromotor impairments: a single-blind randomized controlled crossover pilot study
Abstract
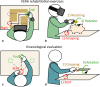
Background: The past decade has seen the emergence of rehabilitation treatments using virtual reality. One of the advantages in using this technology is the potential to create positive motivation, by means of engaging environments and tasks shaped in the form of serious games. The aim of this study is to determine the efficacy of immersive Virtual Environments and weaRable hAptic devices (VERA) for rehabilitation of upper limb in children with Cerebral Palsy (CP) and Developmental Dyspraxia (DD).
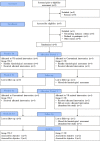
Methods: A two period cross-over design was adopted for determining the differences between the proposed therapy and a conventional treatment. Eight children were randomized into two groups: one group received the VERA treatment in the first period and the manual therapy in the second period, and viceversa for the other group. Children were assessed at the beginning and the end of each period through both the Nine Hole Peg Test (9-HPT, primary outcome) and Kinesiological Measurements obtained during the performing of similar tasks in a real setting scenario (secondary outcomes).
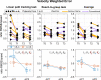
Results: All subjects, not depending from which group they come from, significantly improved in both the performance of the 9-HPT and in the parameters of the kinesiological measurements (movement error and smoothness). No statistically significant differences have been found between the two groups.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that immersive VE and wearable haptic devices is a viable alternative to conventional therapy for improving upper extremity function in children with neuromotor impairments. Trial registration ClinicalTrials, NCT03353623. Registered 27 November 2017-Retrospectively registered, https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03353623.
Keywords: Human Motion Analysis; Rehabilitation; Serious game; Tactile Feedback; Virtual reality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Bortone I, Leonardis D, Solazzi M, Procopio C, Crecchi A, Briscese L, et al. Serious game and wearable haptic devices for neuro motor rehabilitation of children with cerebral palsy. In: Converging clinical and engineering research on neurorehabilitation II. Berlin: Springer; 2017. p. 443–7.
-
- Bortone I, Leonardis D, Solazzi M, Procopio C, Crecchi A, Bonfiglio L, et al. Integration of serious games and wearable haptic interfaces for Neuro Rehabilitation of children with movement disorders: a feasibility study. In: 2017 International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR). IEEE; 2017. p. 1094–9. - PubMed
-
- Wilson P, Green D, Caeyenberghs K, Steenbergen B, Duckworth J. Integrating new technologies into the treatment of CP and DCD. Curr Develop Disord Rep. 2016;3(2):138–151. doi: 10.1007/s40474-016-0083-9. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

