Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index (HAQ-DI) use in modelling disease progression in diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis: an analysis from the EUSTAR database
- PMID: 33115544
- PMCID: PMC7592571
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-020-02329-2
Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index (HAQ-DI) use in modelling disease progression in diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis: an analysis from the EUSTAR database
Abstract
Background: Patients with diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis (dcSSc) have a poor prognosis. The importance of monitoring subjective measures of functioning and disability, such as the Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index (HAQ-DI), is important as dcSSc is rated by patients as worse than diabetes or hemodialysis for quality of life impairment. This European Scleroderma Trials and Research (EUSTAR) database analysis was undertaken to examine the importance of impaired functionality in dcSSc prognosis. The primary objectives were to identify predictors of death and HAQ-DI score progression over 1 year. HAQ-DI score, major advanced organ involvement, and death rate were also used to develop a comprehensive model to predict lifetime dcSSc progression.
Methods: This was an observational, longitudinal study in patients with dcSSc registered in EUSTAR. Death and HAQ-DI scores were, respectively, analyzed by Cox regression and linear regression analyses in relation to baseline covariates. A microsimulation Markov model was developed to estimate/predict natural progression of dcSSc over a patient's lifetime.
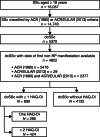
Results: The analysis included dcSSc patients with (N = 690) and without (N = 4132) HAQ-DI score assessments from the EUSTAR database. Baseline HAQ-DI score, corticosteroid treatment, and major advanced organ involvement were predictive of death on multivariable analysis; a 1-point increase in baseline HAQ-DI score multiplied the risk of death by 2.7 (p < 0.001) and multiple advanced major organ involvement multiplied the risk of death by 2.8 (p < 0.05). Multivariable analysis showed that baseline modified Rodnan Skin Score (mRSS) and baseline HAQ-DI score were associated with HAQ-DI score progression at 1 year (p < 0.05), but there was no association between baseline organ involvement and HAQ-DI score progression at 1 year. HAQ-DI score, major advanced organ involvement, and death were successfully used to model long-term disease progression in dcSSc.
Conclusions: HAQ-DI score and major advanced organ involvement were comparable predictors of mortality risk in dcSSc. Baseline mRSS and baseline HAQ-DI score were predictive of HAQ-DI score progression at 1 year, indicating a correlation between these endpoints in monitoring disease progression. It is hoped that this EUSTAR analysis may change physician perception about the importance of the HAQ-DI score in dcSSc.
Keywords: Diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis; EUSTAR registry; HAQ-DI score; Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index.
Conflict of interest statement
Yannick Allanore received fees or grants from Actelion, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Curzion, Inventiva, Roche, and Sanofi.
Oliver Distler had consultancy relationship and/or has received research funding from AbbVie, Actelion, Acceleron Pharma, Amgen, AnaMar, Baecon Discovery, Blade Therapeutics, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Catenion, Competitive Drug Development International Ltd., CSL Behring, ChemomAb, Curzion Pharmaceuticals, Ergonex, Galapagos NV, Glenmark Pharmaceuticals, GSK, Inventiva, Italfarmaco, iQone, iQvia, Lilly, Medac, Medscape, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, Target Bio Science, and UCB in the area of potential treatments of scleroderma and its complications. In addition, Oliver Distler has a patent mir-29 for the treatment of systemic sclerosis issued (US8247389, EP2331143).
Elise Siegert has received speaker fees/compensation for advisory board meetings from Actelion and Boehringer Ingelheim and a grant from Actelion.
László Czirják receives honoraria for consulting services (educational services, scientific articles, participation in advisory boards, clinical trials, other) from AbbVie, Actelion, Boehringer Ingelheim, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Richter, Roche, and UCB.
Patricia E Carreira received fees or grants from Actelion, Boehringer Ingelheim, Emmerald Health Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi, AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma.
Eric Hachulla has no conflicts of interest to declare.
Elisabetta Zanatta had consultancy relationship and/or received fees from Actelion and GSK.
Mengtao Li declares no conflict of interest.
Paolo Airò has received consultancy and/or travel expenses from Bristol Myers Squibb, CSL Behring, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and SOBI.
Fabian A Mendoza had a consultancy relationship with AbbVie, Genentech, and Gilead.
Edoardo Rosato has received research funding from Actelion.
Sylvie Bozzi, Augustin Terlinden, Caroline Amand, and Christina Soubrane are employees of Sanofi R&D, France.
Doerte Huscher has received traveling expenses from Actelion Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Shire International GmbH.
Figures



References
-
- LeRoy EC, Black C, Fleischmajer R, Jablonska S, Krieg T, Medsger TA, Jr, et al. Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis): classification, subsets and pathogenesis. J Rheumatol. 1988;15:202–205. - PubMed
-
- Pokeerbux MR, Giovannelli J, Dauchet L, Mouthon L, Agard C, Lega JC, et al. Survival and prognosis factors in systemic sclerosis: data of a French multicenter cohort, systematic review, and meta-analysis of the literature. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21:86. doi: 10.1186/s13075-019-1867-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

