Robust neutralizing antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 infection persist for months
- PMID: 33115920
- PMCID: PMC7810037
- DOI: 10.1126/science.abd7728
Robust neutralizing antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 infection persist for months
Abstract
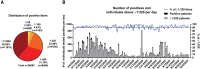
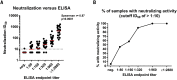
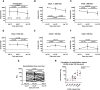
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has caused a global pandemic with millions infected and more than 1 million fatalities. Questions regarding the robustness, functionality, and longevity of the antibody response to the virus remain unanswered. Here, on the basis of a dataset of 30,082 individuals screened at Mount Sinai Health System in New York City, we report that the vast majority of infected individuals with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 experience robust immunoglobulin G antibody responses against the viral spike protein. We also show that titers are relatively stable for at least a period of about 5 months and that anti-spike binding titers significantly correlate with neutralization of authentic SARS-CoV-2. Our data suggest that more than 90% of seroconverters make detectable neutralizing antibody responses. These titers remain relatively stable for several months after infection.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures
Comment in
-
SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: a key target for eliciting persistent neutralizing antibodies.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Feb 26;6(1):95. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00523-5. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 33637679 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Longitudinal dynamics of antibody responses in recovered COVID-19 patients.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Mar 31;6(1):137. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00559-7. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 33790222 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Liu L., To K. K.-W., Chan K.-H., Wong Y.-C., Zhou R., Kwan K.-Y., Fong C. H.-Y., Chen L.-L., Choi C. Y.-K., Lu L., Tsang O. T.-Y., Leung W.-S., To W.-K., Hung I. F.-N., Yuen K.-Y., Chen Z., High neutralizing antibody titer in intensive care unit patients with COVID-19. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 9, 1664–1670 (2020). 10.1080/22221751.2020.1791738 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Long Q. X., Liu B.-Z., Deng H.-J., Wu G.-C., Deng K., Chen Y.-K., Liao P., Qiu J.-F., Lin Y., Cai X.-F., Wang D.-Q., Hu Y., Ren J.-H., Tang N., Xu Y.-Y., Yu L.-H., Mo Z., Gong F., Zhang X.-L., Tian W.-G., Hu L., Zhang X.-X., Xiang J.-L., Du H.-X., Liu H.-W., Lang C.-H., Luo X.-H., Wu S.-B., Cui X.-P., Zhou Z., Zhu M.-M., Wang J., Xue C.-J., Li X.-F., Wang L., Li Z.-J., Wang K., Niu C.-C., Yang Q.-J., Tang X.-J., Zhang Y., Liu X.-M., Li J.-J., Zhang D.-C., Zhang F., Liu P., Yuan J., Li Q., Hu J.-L., Chen J., Huang A.-L., Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients with COVID-19. Nat. Med. 26, 845–848 (2020). 10.1038/s41591-020-0897-1 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

