Identification of SARS-CoV-2 entry inhibitors among already approved drugs
- PMID: 33116249
- PMCID: PMC7594953
- DOI: 10.1038/s41401-020-00556-6
Identification of SARS-CoV-2 entry inhibitors among already approved drugs
Abstract
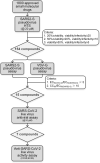
To discover effective drugs for COVID-19 treatment amongst already clinically approved drugs, we developed a high throughput screening assay for SARS-CoV-2 virus entry inhibitors using SARS2-S pseudotyped virus. An approved drug library of 1800 small molecular drugs was screened for SARS2 entry inhibitors and 15 active drugs were identified as specific SARS2-S pseudovirus entry inhibitors. Antiviral tests using native SARS-CoV-2 virus in Vero E6 cells confirmed that 7 of these drugs (clemastine, amiodarone, trimeprazine, bosutinib, toremifene, flupenthixol, and azelastine) significantly inhibited SARS2 replication, reducing supernatant viral RNA load with a promising level of activity. Three of the drugs were classified as histamine receptor antagonists with clemastine showing the strongest anti-SARS2 activity (EC50 = 0.95 ± 0.83 µM). Our work suggests that these 7 drugs could enter into further in vivo studies and clinical investigations for COVID-19 treatment.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; approved drug library; clemastine; high throughput screening assay; histamine receptor antagonists; virus entry inhibitors.
© 2020. CPS and SIMM.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Lan J, Ge J, Yu J, Shan S, Zhou H, Fan S, et al. Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor. Nature. 2020;581:215–20. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

