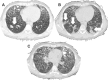
Eculizumab, SARS-CoV-2 and atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome
- PMID: 33117528
- PMCID: PMC7543344
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfaa166
Eculizumab, SARS-CoV-2 and atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome
Abstract
Atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS) treatment consists of eculizumab. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 causes severe pneumonia and endothelial injury that leads to a prothrombotic state that may be complicated by macrovascular and microvascular thrombosis. Complement activation is thought to contribute to endothelial injury and there are at least seven ongoing clinical trials testing six different anti-complement strategies for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), including eculizumab. We herein report on a kidney transplant patient with aHUS on chronic eculizumab therapy that developed severe COVID-19 despite eculizumab administration early in the course of the disease. Although eculizumab was unable to prevent the development of severe endothelial cell injury, as assessed by increasing D-dimer levels from 292 to 10 586 ng/mL, the patient eventually recovered following dexamethasone and convalescent plasma administration.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; aHUS; complement; eculizumab; kidney transplant.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of ERA-EDTA.
Figures
Comment in
-
Complement and protection from tissue injury in COVID-19.Clin Kidney J. 2020 Oct 4;13(5):734-738. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfaa196. eCollection 2020 Oct. Clin Kidney J. 2020. PMID: 33123353 Free PMC article.
-
Additional eculizumab dose and tacrolimus discontinuation for treatment of COVID-19 in a kidney transplant recipient with aHUS.Ther Apher Dial. 2022 Feb;26(1):250-251. doi: 10.1111/1744-9987.13710. Epub 2021 Jul 24. Ther Apher Dial. 2022. PMID: 34272820 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Gao T, Hu M, Zhang X. et al. Highly pathogenic coronavirus N protein aggravates lung injury by MASP-2-mediated complement over-activation. medRxiv 2020; doi: 10.1101/2020.03.29.20041962
-
- Horby P, Lim W, Emberson J. et al. Effect of dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: Preliminary Report Recovery Collaborative Group. medRxiv 2020; doi: 10.1101/2020.06.22.20137273
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous