Synthesis and characterization of a tert- butyl ester-substituted titanocene dichloride: t-BuOOCCp2TiCl2
- PMID: 33117564
- PMCID: PMC7534228
- DOI: 10.1107/S2056989020011834
Synthesis and characterization of a tert- butyl ester-substituted titanocene dichloride: t-BuOOCCp2TiCl2
Abstract
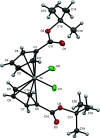
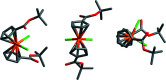
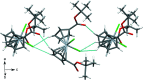
Bis[η5-(tert-butoxyca-rbonyl)-cyclo-penta-dien-yl]di-chlorido-titanium(IV), [Ti(C10H13O2)2Cl2], was synthesized from LiCpCOOt-Bu using TiCl4, and was characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction and 1H NMR spectroscopy. The distorted tetra-hedral geometry about the central titanium atom is relatively unchanged compared to Cp2TiCl2. The complex exhibits elongation of the titanium-cyclo-penta-dienyl centroid distances [2.074 (3) and 2.070 (3) Å] and a contraction of the titanium-chlorine bond lengths [2.3222 (10) Å and 2.3423 (10) Å] relative to Cp2TiCl2. The dihedral angle formed by the planes of the Cp rings [52.56 (13)°] is smaller than seen in Cp2TiCl2. Both ester groups extend from the same side of the Cp rings, and occur on the same side of the complex as the chlorido ligands. The complex may serve as a convenient synthon for titanocene complexes with carboxyl-ate anchoring groups for binding to metal oxide substrates.
Keywords: carboxylate anchoring group; crystal structure; metallocene; titanocene.
© McCarthy et al. 2020.
Figures
References
-
- Bruker (2013). SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Bruker (2016). SADABS. Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Bruker (2017). APEX3. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Ceballos-Torres, J., Gómez-Ruiz, S., Fajardo, M., Pinar, A. B. & Prashar, S. (2019). J. Organomet. Chem. 899, 120890.
-
- Clearfield, A., Warner, D. K., Saldarriaga-Molina, C. H., Ropal, R. & Bernal, I. (1975). Can. J. Chem. 53, 1622–1629.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
