Emerging Roles of Exosomal Circular RNAs in Cancer
- PMID: 33117799
- PMCID: PMC7578227
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.568366
Emerging Roles of Exosomal Circular RNAs in Cancer
Abstract
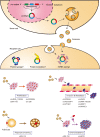
Circular RNA (circRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA that forms a covalently closed continuous loop. The expression pattern of circRNA varies among cell types and tissues, and many circRNAs are aberrantly expressed in various cancers. Aberrantly expressed circRNAs have been shown to play crucial roles in carcinogenesis, functioning as microRNA sponges or new templates for protein translation. Recent research has shown that circRNAs are enriched in exosomes. Exosomes are secretory vesicles that mediate intercellular communication through the delivery of cargo, including proteins, lipids, DNA, and RNA. Exosome-mediated crosstalk between cancer cells and the tumor microenvironment promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, angiogenesis, and immune escape, and thus may contribute to cancer invasion and metastasis. In this review, we discuss the biological functions of exosomal circRNAs and their significance in cancer progression. Additionally, we discuss the potential clinical applications of exosomal circRNAs as biomarkers and in cancer therapy.
Keywords: biomarker; cancer progression; circRNA; circular RNA; exosomal circRNA; exosome.
Copyright © 2020 Seimiya, Otsuka, Iwata, Shibata, Tanaka, Suzuki and Koike.
Figures
References
-
- Bachmayr-Heyda A., Reiner A. T., Auer K., Sukhbaatar N., Aust S., Bachleitner-Hofmann T., et al. (2015). Correlation of circular RNA abundance with proliferation–exemplified with colorectal and ovarian cancer, idiopathic lung fibrosis, and normal human tissues. Sci. Rep. 5:8057. 10.1038/srep08057 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

