LncRNA-mediated posttranslational modifications and reprogramming of energy metabolism in cancer
- PMID: 33119215
- PMCID: PMC7896749
- DOI: 10.1002/cac2.12108
LncRNA-mediated posttranslational modifications and reprogramming of energy metabolism in cancer
Abstract
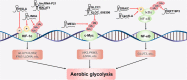
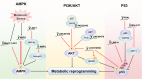
Altered metabolism is a hallmark of cancer, and the reprogramming of energy metabolism has historically been considered a general phenomenon of tumors. It is well recognized that long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) regulate energy metabolism in cancer. However, lncRNA-mediated posttranslational modifications and metabolic reprogramming are unclear at present. In this review, we summarized the current understanding of the interactions between the alterations in cancer-associated energy metabolism and the lncRNA-mediated posttranslational modifications of metabolic enzymes, transcription factors, and other proteins involved in metabolic pathways. In addition, we discuss the mechanisms through which these interactions contribute to tumor initiation and progression, and the key roles and clinical significance of functional lncRNAs. We believe that an in-depth understanding of lncRNA-mediated cancer metabolic reprogramming can help to identify cellular vulnerabilities that can be exploited for cancer diagnosis and therapy.
Keywords: cancer metabolism; enzyme; long noncoding RNA; metabolic reprogramming; posttranslational modification.
© 2020 The Authors. Cancer Communications published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd. on behalf of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
LncRNAs regulate metabolism in cancer.Int J Biol Sci. 2020 Feb 10;16(7):1194-1206. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.40769. eCollection 2020. Int J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32174794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non-coding RNAs involved in cancer metabolic reprogramming.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Feb;76(3):495-504. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2946-1. Epub 2018 Oct 19. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30341461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The molecular mechanisms of LncRNA-correlated PKM2 in cancer metabolism.Biosci Rep. 2019 Nov 29;39(11):BSR20192453. doi: 10.1042/BSR20192453. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31654067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non‑coding RNAs: Key regulators involved in metabolic reprogramming in cancer (Review).Oncol Rep. 2021 May;45(5):54. doi: 10.3892/or.2021.8005. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Oncol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33760177 Review.
-
Amino acid metabolism regulated by lncRNAs: the propellant behind cancer metabolic reprogramming.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 May 1;21(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01116-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37127605 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Constructed Risk Prognosis Model Associated with Disulfidptosis lncRNAs in HCC.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 18;24(24):17626. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417626. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139458 Free PMC article.
-
Developing a RiskScore Model based on Angiogenesis-related lncRNAs for Colon Adenocarcinoma Prognostic Prediction.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(17):2449-2466. doi: 10.2174/0109298673277243231108071620. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37961859
-
lncRNA JPX modulates malignant progress of osteosarcoma through targeting miR-33a-5p and PNMA1 regulatory loop.Transl Oncol. 2022 Nov;25:101504. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2022.101504. Epub 2022 Sep 5. Transl Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36067544 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the roles and molecular mechanisms of RNA binding proteins in the sorting of noncoding RNAs into exosomes during tumor progression.J Adv Res. 2024 Nov;65:105-123. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2023.11.029. Epub 2023 Nov 27. J Adv Res. 2024. PMID: 38030125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The metabolism-related lncRNA signature predicts the prognosis of breast cancer patients.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 12;14(1):3500. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-53716-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38347041 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

