Plasmonic Sensors for Extracellular Vesicle Analysis: From Scientific Development to Translational Research
- PMID: 33119256
- PMCID: PMC8423498
- DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.0c07581
Plasmonic Sensors for Extracellular Vesicle Analysis: From Scientific Development to Translational Research
Abstract
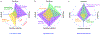
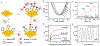
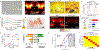
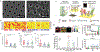
Extracellular vesicles (EVs), actively shed from a variety of neoplastic and host cells, are abundant in blood and carry molecular markers from parental cells. For these reasons, EVs have gained much interest as biomarkers of disease. Among a number of different analytical methods that have been developed, surface plasmon resonance (SPR) stands out as one of the ideal techniques given its sensitivity, robustness, and ability to miniaturize. In this Review, we compare different SPR platforms for EV analysis, including conventional SPR, nanoplasmonic sensors, surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, and plasmonic-enhanced fluorescence. We discuss different surface chemistries used to capture targeted EVs and molecularly profile their proteins and RNAs. We also highlight these plasmonic platforms' clinical applications, including cancers, neurodegenerative diseases, and cardiovascular diseases. Finally, we discuss the future perspective of plasmonic sensing for EVs and their potentials for commercialization and clinical translation.
Keywords: biomarkers; biosensing; diagnostics; extracellular vesicles; nanoplasmonics; plasmon-enhanced fluorescence; surface plasmon resonance; surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy.
Figures
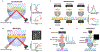
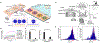
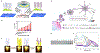

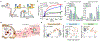
References
-
- Mathieu M; Martin-Jaular L; Lavieu G; Théry C Specificities of Secretion and Uptake of Exosomes and Other Extracellular Vesicles for Cell-to-Cell Communication. Nat Cell Biol 2019, 21, 9–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

