Effect of downregulation of serum MMP-3 levels by traditional Chinese medicine ingredients combined with methotrexate on the progression of bone injury in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 33120813
- PMCID: PMC7581142
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022841
Effect of downregulation of serum MMP-3 levels by traditional Chinese medicine ingredients combined with methotrexate on the progression of bone injury in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: A large number of clinical studies have confirmed that after treatment with traditional Chinese medicine components such as sinomenine (SIN), the matrix -metalloproteinase3 (MMP-3) level of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) shows a significant decrease, whereas MMP-3 can be involved in degrading bone matrix in humans, so in the progression of bone and joint injury in patients with RA, serum MMP-3 can be used as an important biochemical marker. The traditional Chinese medicine components commonly used in clinical practice include total glucosides of paeony (TGP), SIN, and tripterygium glycosides, which have the characteristics of disease-modifyinganti-rheumatic drugs and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, while they can reduce the toxic side effects of methotrexate (MTX), and their combination with other drugs such as MTX and leflunomide (HWA486) has become an important regimen for the treatment of RA in clinical practice. Therefore, we designed this study protocol to evaluate the adjuvant effect of commonly used traditional Chinese medicine components combined with MTX in the treatment of osteoarticular injury in RA.
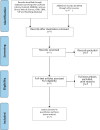
Methods: The search time was set from January 2000 to September 2020 in this study. EMBASE database, Cochrane Library, PubMed, Web of Science, Science Direct, Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure, China Biology Medicine disc (CBM), Chinese Scientifific Journals Database (VIP), and Wanfang Database were used as search sources to select the traditional Chinese medicine components that reduce MMP-3 and use MTX in the treatment of RA. Clinical randomized controlled trials were used, and inclusion criteria and exclusion criteria were set for screening. In this study, MMP-3, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C-reactive protein (CRP), cyclic peptide containing citrulline (CCP) and rheumatoid factor (RF) were used as the main outcomes, and the improvement of Disease Activity Score 28 (DAS28), joint bone mineral density, Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI), and other clinically relevant symptoms was selected as the secondary outcomes. Revman software version 5.3 was used for statistical analysis of data and risk assessment of deviation in this meta-analysis. In this study, one researcher performed study direction selection, literature inquiry, and literature download, and 2 independent reviewers performed literature data extraction and literature quality assessment. Dichotomized data are expressed as relative risk, continuous data are expressed as mean difference or standard mean difference, and finally fixed-effect model or random-effect model is used for synthesis according to the heterogeneity of data.
Results: To evaluate the effect of downregulation of MMP-3 level by traditional Chinese medicine components combined with MTX on the progression of bone injury in patients with RA by serum MMP-3, ESR, CRP, CCP, and RF.
Conclusion: This study protocol can be used to evaluate the efficacy and safety of traditional Chinese medicine components combined with MTX in the treatment of bone injury in patients with RA.
Ethics and dissemination: This study is a secondary study based on the published clinical research; therefore, approval from an ethics committee is not required for this study. In accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis Protocol (PRISMA-P), the results of this study will be published in peer-reviewed scientific journals and conference papers. REGISTRATION NUMBER:: is INPLASY202090064.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effectiveness and safety of Tripterygium wilfordii glycosides combined with disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 40 randomized controlled trials.Phytother Res. 2021 Jun;35(6):2902-2924. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6996. Epub 2020 Dec 23. Phytother Res. 2021. PMID: 33368709
-
Efficacy and safety of total glucosides of paeony combined with methotrexate and leflunomide for active rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 Jun 17;13:1969-1984. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S207226. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 31354242 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese herbal medicine si-miao-san decoction for acute gouty arthritis: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Aug 7;99(32):e21510. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000021510. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32769889 Free PMC article.
-
[Efficacy of Hebi Formula Combined Methotrexate on Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients with Dis- harmony of Gan and Pi Syndrome and Its Effects on Serum MMP-3 and RANK/RANKL/OPG Expressions].Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2016 Oct;36(10):1197-1201. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 30641006 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
[Systematic reviews of effects of Tripterygium Glycosides Tablets on pro-inflammatory factors in rheumatoid arthritis].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020 Feb;45(4):764-774. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20191024.401. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32237476 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Total Flavonoids of Rhizoma Drynariae Ameliorate Bone Growth in Experimentally Induced Tibial Dyschondroplasia in Chickens via Regulation of OPG/RANKL Axis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 May 26;13:881057. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.881057. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35694251 Free PMC article.
-
Interpreting the pharmacological mechanisms of Juanbi recipe on rheumatoid arthritis through network pharmacology, molecular docking.Ann Jt. 2024 Jul 12;9:23. doi: 10.21037/aoj-23-72. eCollection 2024. Ann Jt. 2024. PMID: 39114420 Free PMC article.
-
Benefit-risk assessment of traditional Chinese medicine preparations of sinomenine using multicriteria decision analysis (MCDA) for patients with rheumatoid arthritis.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Feb 6;23(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-03864-6. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 36747185 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive overview of triptolide utilizing nanotechnology and its potential applications in prostate diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 17;16:1592066. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1592066. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40599799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathomechanisms of bone loss in rheumatoid arthritis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 17;9:962969. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.962969. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36059831 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hoes JN, Bultink IE, Lems WF. Management of osteoporosis in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Expert Opin Pharmacother 2015;16:559–71. - PubMed
-
- Geraldo-Flores NA, Merlos-López RJ, Rodríguez-Wong JA, et al. The severity of rheumatoid arthritis as a timely predictor of instability in the asymptomatic cervical spine. Acta Ortop Mex 2018;32:342–6. - PubMed
-
- Zhang YY, Wang J, Jiang P, et al. Efficacy of Hebi Formula Combined Methotrexate on Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients with Dis- harmony of Gan and Pi Syndrome and Its Effects on Serum MMP-3 and RANK/RANKL/OPG Expressions. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2016;36:1197–201. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous