COVID-19-Associated Neurological Disorders: The Potential Route of CNS Invasion and Blood-Brain Relevance
- PMID: 33120941
- PMCID: PMC7692725
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9112360
COVID-19-Associated Neurological Disorders: The Potential Route of CNS Invasion and Blood-Brain Relevance
Abstract
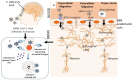
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a novel human coronavirus that has sparked a global pandemic of the coronavirus disease of 2019 (COVID-19). The virus invades human cells through the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor-driven pathway, primarily targeting the human respiratory tract. However, emerging reports of neurological manifestations demonstrate the neuroinvasive potential of SARS-CoV-2. This review highlights the possible routes by which SARS-CoV-2 may invade the central nervous system (CNS) and provides insight into recent case reports of COVID-19-associated neurological disorders, namely ischaemic stroke, encephalitis, encephalopathy, epilepsy, neurodegenerative diseases, and inflammatory-mediated neurological disorders. We hypothesize that SARS-CoV-2 neuroinvasion, neuroinflammation, and blood-brain barrier (BBB) dysfunction may be implicated in the development of the observed disorders; however, further research is critical to understand the detailed mechanisms and pathway of infectivity behind CNS pathogenesis.
Keywords: CNS; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; blood-brain barrier; cerebrovascular; neurological disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Pneumonia of unknown cause – China. [(accessed on 3 June 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/csr/don/05-january-2020-pneumonia-of-unkown-cause-ch...
-
- World map. [(accessed on 3 June 2020)]; Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/global-covid-19/world-map.html.
-
- Weekly Operational Update on COVID-19. [(accessed on 4 September 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/w....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

