Size-Exclusion Chromatography as a Technique for the Investigation of Novel Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer
- PMID: 33121160
- PMCID: PMC7693800
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12113156
Size-Exclusion Chromatography as a Technique for the Investigation of Novel Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer
Abstract
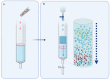
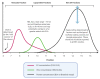
Cancer cells release extracellular vesicles, which are a rich target for biomarker discovery and provide a promising mechanism for liquid biopsy. Size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) is an increasingly popular technique, which has been rediscovered for the purposes of extracellular vesicle (EV) isolation and purification from diverse biofluids. A systematic review was undertaken to identify all papers that described size exclusion as their primary EV isolation method in cancer research. In all, 37 papers were identified and discussed, which showcases the breadth of applications in which EVs can be utilised, from proteomics, to RNA, and through to functionality. A range of different methods are highlighted, with Sepharose-based techniques predominating. EVs isolated using SEC are able to identify cancer cells, highlight active pathways in tumourigenesis, clinically distinguish cohorts, and remain functionally active for further experiments.
Keywords: SEC; biomarkers; cancer; exosomes; extracellular vesicles; size-exclusion chromatography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kim J.W., Wieckowski E., Taylor D.D., E Reichert T., Watkins S., Whiteside T.L. Fas ligand-positive membranous vesicles isolated from sera of patients with oral cancer induce apoptosis of activated T lymphocytes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005;11:1010–1020. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

