YTHDF2 mediates the mRNA degradation of the tumor suppressors to induce AKT phosphorylation in N6-methyladenosine-dependent way in prostate cancer
- PMID: 33121495
- PMCID: PMC7599101
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-020-01267-6
YTHDF2 mediates the mRNA degradation of the tumor suppressors to induce AKT phosphorylation in N6-methyladenosine-dependent way in prostate cancer
Abstract
Background: N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most abundant modification in mRNA of humans. Emerging evidence has supported the fact that m6A is comprehensively involved in various diseases especially cancers. As a crucial reader, YTHDF2 usually mediates the degradation of m6A-modified mRNAs in m6A-dependent way. However, the function and mechanisms of m6A especially YTHDF2 in prostate cancer (PCa) still remain elusive.
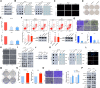
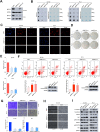
Methods: To investigate the functions and mechanisms of YTHDF2 in PCa, in vitro, in vivo biofunctional assays and epigenetics experiments were performed. Endogenous expression silencing of YTHDF2 and METTL3 was established with lentivirus-based shRNA technique. Colony formation, flow cytometry and trans-well assays were performed for cell function identifications. Subcutaneous xenografts and metastatic mice models were combined with in vivo imaging system to investigate the phenotypes when knocking down YTHDF2 and METTL3. m6A RNA immunoprecipitation (MeRIP) sequencing, mRNA sequencing, RIP-RT-qPCR and bioinformatics analysis were mainly used to screen and validate the direct common targets of YTHDF2 and METTL3. In addition, TCGA database was also used to analyze the expression pattern of YTHDF2, METTL3 and the common target LHPP in PCa, and their correlation with clinical prognosis.
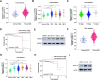
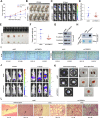
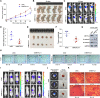
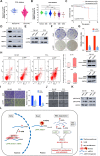
Results: The upregulated YTHDF2 and METTL3 in PCa predicted a worse overall survival rate. Knocking down YTHDF2 or METTL3 markedly inhibited the proliferation and migration of PCa in vivo and in vitro. LHPP and NKX3-1 were identified as the direct targets of both YTHDF2 and METTL3. YTHDF2 directly bound to the m6A modification sites of LHPP and NKX3-1 to mediate the mRNA degradation. Knock-down of YTHDF2 or METTL3 significantly induced the expression of LHPP and NKX3-1 at both mRNA and protein level with inhibited phosphorylated AKT. Overexpression of LHPP and NKX3-1 presented the consistent phenotypes and AKT phosphorylation inhibition with knock-down of YTHDF2 or METTL3. Phosphorylated AKT was consequently confirmed as the downstream of METTL3/YTHDF2/LHPP/NKX3-1 to induce tumor proliferation and migration.
Conclusion: We propose a novel regulatory mechanism in which YTHDF2 mediates the mRNA degradation of the tumor suppressors LHPP and NKX3-1 in m6A-dependent way to regulate AKT phosphorylation-induced tumor progression in prostate cancer. We hope our findings may provide new concepts of PCa biology.
Keywords: M6A; Prostate cancer; RNA degradation; RNA methylation; YTHDF2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Activation of the KDM5A/miRNA-495/YTHDF2/m6A-MOB3B axis facilitates prostate cancer progression.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Oct 21;39(1):223. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01735-3. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33087165 Free PMC article.
-
METTL3 regulates Ambra1 expression in an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner to promote mantle cell lymphoma progression.J Transl Med. 2025 Jul 1;23(1):703. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06647-4. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40597351 Free PMC article.
-
m6 A modification of lncRNA PCAT6 promotes bone metastasis in prostate cancer through IGF2BP2-mediated IGF1R mRNA stabilization.Clin Transl Med. 2021 Jun;11(6):e426. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.426. Clin Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34185427 Free PMC article.
-
Review of METTL3 in colorectal cancer: From mechanisms to the therapeutic potential.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Oct;277(Pt 2):134212. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.134212. Epub 2024 Jul 26. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 39069066 Review.
-
The role of the methyltransferase METTL3 in prostate cancer: a potential therapeutic target.BMC Cancer. 2024 Jan 2;24(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11741-1. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38166703 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel insights into the regulatory role of N6-methyladenosine methylation modified autophagy in sepsis.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Dec 18;15(24):15676-15700. doi: 10.18632/aging.205312. Epub 2023 Dec 18. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 38112620 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuation of IFN signaling due to m6A modification of the host epitranscriptome promotes EBV lytic reactivation.J Biomed Sci. 2023 Mar 14;30(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s12929-023-00911-9. J Biomed Sci. 2023. PMID: 36918845 Free PMC article.
-
N6-methyladenosine writer METTL3 accelerates the sepsis-induced myocardial injury by regulating m6A-dependent ferroptosis.Apoptosis. 2023 Apr;28(3-4):514-524. doi: 10.1007/s10495-022-01808-y. Epub 2023 Jan 16. Apoptosis. 2023. PMID: 36645573
-
Liquid-liquid phase separation in tumor biology.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Jul 8;7(1):221. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01076-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 35803926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decoding m6A mRNA methylation by reader proteins in liver diseases.Genes Dis. 2023 Apr 13;11(2):711-726. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2023.02.054. eCollection 2024 Mar. Genes Dis. 2023. PMID: 37692496 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

