Disordered leptin and ghrelin bioactivity in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS): a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 33121521
- PMCID: PMC7596938
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-020-01988-w
Disordered leptin and ghrelin bioactivity in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS): a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Adolescents with scoliosis consistently demonstrate lower body weight, lean muscle mass, and bone mineral density than healthy adolescent counterparts. Recent studies have focused on understanding how leptin and ghrelin signaling may play a role in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS). In our current study, we aim to evaluate the serum levels of leptin, soluble leptin receptor (sOB-R), and ghrelin in AIS patients through systematic review and meta-analysis.
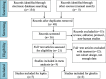
Methods: We conducted our systematic review by searching the keywords in online databases including PubMed, Embase, Cochrane, Elsevier, Springer, and Web of Science from the time of database inception to January 2020. Inclusion criteria were studies that measure leptin, soluble leptin receptor (sOB-R), and ghrelin levels in AIS patients. Selection of studies, assessment of study quality, and data extraction were performed by two reviewers independently. Then, data was analyzed to calculate the mean difference and 95% confidence interval (CI).
Results: Seven studies concerning leptin/sOB-R and three studies concerning ghrelin were qualified for meta-analysis (one study concerning both leptin and ghrelin). Serum leptin of patients with AIS were significantly lower when compared with healthy controls, with the weighted mean difference (WMD) of - 0.95 (95% CI - 1.43 to - 0.48, p < 0.0001) after reducing the heterogeneity using six studies for meta-analysis, while sOB-R and ghrelin level was significantly higher in AIS group when compared with control group, with the WMD of 2.64 (95% CI 1.60 to 3.67, p < 0.001) and 1.42 (95% CI 0.48 to 2.35, p = 0.003), respectively.
Conclusion: Our current meta-analysis showed that serum level of leptin in AIS patients was significantly lower when compared with control subjects, while serum sOB-R and ghrelin levels were significantly higher in AIS patients. More clinical studies are still required to further validate the predictive value of leptin or ghrelin for the curve progression for AIS patients.
Keywords: Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis; Ghrelin; Leptin; Meta-analysis; Soluble leptin receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Leptin in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis - A meta-analysis.J Clin Neurosci. 2020 Jan;71:124-128. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2019.08.106. Epub 2019 Sep 4. J Clin Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31493992
-
Abnormal leptin bioavailability in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: an important new finding.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012 Apr 1;37(7):599-604. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e318227dd0c. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012. PMID: 21681139
-
Are volumetric bone mineral density and bone micro-architecture associated with leptin and soluble leptin receptor levels in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis?--A case-control study.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 6;9(2):e87939. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087939. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24516571 Free PMC article.
-
Association between calcium-phosphorus balance and adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A meta-analysis.Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2019 Nov;53(6):468-473. doi: 10.1016/j.aott.2019.08.012. Epub 2019 Oct 16. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2019. PMID: 31628002 Free PMC article.
-
Etiologic theories of idiopathic scoliosis: autonomic nervous system and the leptin-sympathetic nervous system concept for the pathogenesis of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.Stud Health Technol Inform. 2008;140:197-207. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2008. PMID: 18810025 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Adipokines in Spinal Disease: A Narrative Review.JOR Spine. 2025 Jun 3;8(2):e70083. doi: 10.1002/jsp2.70083. eCollection 2025 Jun. JOR Spine. 2025. PMID: 40470308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction between Selected Adipokines and Musculoskeletal and Cardiovascular Systems: A Review of Current Knowledge.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 9;24(24):17287. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417287. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differences in Pubertal Curve Progression among Females with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Using Pregnenolone Therapy: A Retrospective Case-Controlled Series.J Clin Med. 2024 Jan 30;13(3):788. doi: 10.3390/jcm13030788. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38337480 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Muscle Biomarkers in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis.J Clin Med. 2023 Dec 11;12(24):7616. doi: 10.3390/jcm12247616. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38137689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Imbalances and Bone Remodeling Agents in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Study in Postmenarcheal Girls.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 27;24(17):13286. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713286. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686090 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Watanabe K, Ohashi M, Hirano T, Katsumi K, Mizouchi T, Tashi H, et al. Health-related quality of life in non-operated patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in the middle years: a mean 25-year follow-up study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2019 Aug 27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

