Blood Banking and Transfusion Medicine Challenges During the COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 33121624
- PMCID: PMC7414314
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cll.2020.08.013
Blood Banking and Transfusion Medicine Challenges During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
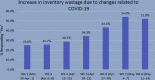
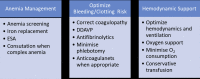
SARS-CoV-2 (also known as COVID-19) has been an unprecedented challenge in many parts of the medical field with blood banking being no exception. COVID-19 has had a distinctly negative effect on our blood collection nationwide forcing blood banks, blood centers, and the US government to adopt new policies to adapt to a decreased blood supply as well as to protect our donors from COVID-19. These policies can be seen distinctly in patient blood management and blood bank operations. We are also faced with developing policies and procedures for a nontraditional therapy, convalescent plasma; its efficacy and safety is still not completely elucidated as of yet.
Keywords: Blood banking; Blood shortage; Blood wastage; COVID-19; Convalescent plasma; FDA donation policies; Transfusion medicine.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure Dr. Majed A. Refaai has received consulting fees and/or research funding from CSL Behring, Octapharma, Bayer, Instrumentation Laboratory, and iLine microsystems and has received speaking fees from CSL Behring.The other Authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Paules C.I., Marston H.D., Fauci A.S. Coronavirus infections—more than just the common cold. JAMA. 2020;323(8):707–708. - PubMed
-
- Sultan S., Altayar O., Siddique S.M., et al. AGA Institute rapid review of the gastrointestinal and liver manifestations of COVID-19, meta-analysis of international data, and recommendations for the consultative management of patients with COVID-19. Gastroenterology. 2020;159(1):320–334.e27. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous