Cellular and molecular imaging for stem cell tracking in neurological diseases
- PMID: 33122254
- PMCID: PMC8005893
- DOI: 10.1136/svn-2020-000408
Cellular and molecular imaging for stem cell tracking in neurological diseases
Abstract
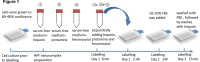
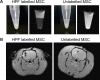
Stem cells (SCs) are cells with strong proliferation ability, multilineage differentiation potential and self-renewal capacity. SC transplantation represents an important therapeutic advancement for the treatment strategy of neurological diseases, both in the preclinical experimental and clinical settings. Innovative and breakthrough SC labelling and tracking technologies are widely used to monitor the distribution and viability of transplanted cells non-invasively and longitudinally. Here we summarised the research progress of the main tracers, labelling methods and imaging technologies involved in current SC tracking technologies for various neurological diseases. Finally, the applications, challenges and unresolved problems of current SC tracing technologies were discussed.
Keywords: MRI; brain; technique.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Visualizing stem cells in vivo using magnetic resonance imaging.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2022 Mar;14(2):e1760. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1760. Epub 2021 Oct 15. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2022. PMID: 34651465 Review.
-
Stem Cell Tracking Technologies for Neurological Regenerative Medicine Purposes.Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:2934149. doi: 10.1155/2017/2934149. Epub 2017 Sep 12. Stem Cells Int. 2017. PMID: 29138636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Distinctive MRI-Based Absolute Bias Correction Protocol for the Potential Labelling and In Vivo Tracking of Stem Cells in a TBI Mice Model.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2150:93-111. doi: 10.1007/7651_2019_277. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31802432
-
Molecular imaging and tracking stem cells in neurosciences.Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1052:195-201. doi: 10.1007/7651_2013_27. Methods Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23640257 Review.
-
Long-term MRI tracking of dual-labeled adipose-derived stem cells homing into mouse carotid artery injury.Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:5191-203. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S35647. Epub 2012 Oct 2. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012. PMID: 23125528 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Emerging strategies for nerve repair and regeneration in ischemic stroke: neural stem cell therapy.Neural Regen Res. 2024 Nov 1;19(11):2430-2443. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.391313. Epub 2023 Dec 21. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 38526280 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of different 89Zr-labeled synthons for direct labeling and tracking of white blood cells and stem cells in healthy athymic mice.Sci Rep. 2022 Sep 19;12(1):15646. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-19953-4. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36123386 Free PMC article.
-
Biomaterial application strategies to enhance stem cell-based therapy for ischemic stroke.World J Stem Cells. 2022 Dec 26;14(12):851-867. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i12.851. World J Stem Cells. 2022. PMID: 36619694 Free PMC article.
-
Optical molecular imaging and theranostics in neurological diseases based on aggregation-induced emission luminogens.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022 Nov;49(13):4529-4550. doi: 10.1007/s00259-022-05894-7. Epub 2022 Jul 4. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35781601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial DNA as a target for analyzing the biodistribution of cell therapy products.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 4;14(1):7934. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56591-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38575614 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
